Search Results
Literacy Practice: 3-2-1 Strategy
Use this lesson plan and the provided template to have your students practice the 3-2-1 strategy. This literacy strategy is a quick way to check students’ understanding of a concept, reading or lesson. It helps them summarize and organize their thoughts by listing three responses to one prompt, two responses to another prompt and one response to a final prompt.

A Crumbling Exoplanet and Marsupial Moles
Incorporate articles from the March issue of Science News to learn how scientists are using data from the James Webb Space Telescope to find out what exoplanets might be made of and investigate common characteristics among organisms using phylogenetic trees and cladograms.
Exoplanet spills its guts
Scientists just caught a rare glimpse of an exoplanet’s innards. Learn how scientists use wavelength data from the James Webb Space Telescope to figure out what exoplanets might be made of. Answer questions about the value of personification as a literary device, all the while discussing how knowledge gleaned from one discovery can help scientists answer new and lingering questions.
Uncovering the ancestry of the marsupial mole
Use scientists’ latest findings about marsupial moles to have students explore natural selection. Students will use figures that depict evolutionary relationships among organisms — phylogenetic trees and cladograms — to trace ancestry and common characteristics. Then they will apply this knowledge by investigating common characteristics of different taxonomic groups associated with the marsupial mole, illustrating why this animal has been particularly hard to categorize and study.
Fungal Solutions
Across the planet, people throw away over
two billion metric tons of waste every year. That waste feeds into environmental problems from climate change to pollution. So how can we reduce the amount of waste we produce? In this activity, students will categorize and record the waste they produce daily and reflect on the amount of “invisible” waste produced before they receive products. Students will then identify solutions for reducing each category of waste.

All About Technically Fiction, Concept Maps and Yellowstone’s Hydrothermal Explosions
Pair these lesson plans with articles from the March issue of Science News Explores to incorporate fictional phenomena from any Technically Fiction article with your students, download a template for concept maps and have students answer questions about Yellowstone National Park’s geologic history.
All about Technically Fiction: An article type from Science News Explores
Use this lesson plan to learn about an article type called Technically Fiction that is published by Science News Explores in print and online. Technically Fiction articles focus on a fictional phenomenon and explain whether it could be possible and the science it would take to make it a reality. You can also access a lesson plan template that can be used with any Technically Fiction article.
Literacy Practice: Concept Map
Use this lesson plan and the provided template to have your students practice creating concept maps for any article. This literacy strategy boosts critical thinking and reading retention by having students organize information and connect important ideas, concepts and terms.
Slumbering water volcanoes
ooking for exciting and important applications of the phases of matter? Have students answer a set of questions relating changes in pressure to changes in states of matter. Learn about how hydrothermal explosions occur and the risk for these at Yellowstone National Park, all while discussing how geologists use core data to piece together geological history.
Making use of nature’s designs
New discoveries about the natural world can inspire the design of human-made objects. In this activity, students will learn about how the overlapping feathers on birds’ wings prompted engineers to reimagine the design of aircraft wings. Students will explain how this is an example of bioinspired design and then create their own bioinspired designs.
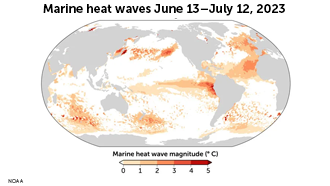
Analysis of marine heat waves
Global temperatures are at an all-time high due to the compounded effects of climate change and El Nino. Oceans around the world are warming at an alarming rate. In summer 2023, some 40 percent of the world’s oceans were affected by heat waves.

Emotional Responses and Nanonoodles
Check out these lesson plans paired to articles from the February issue of Science News to compare class survey data about where different emotional responses are felt in their bodies to two recent studies and have students apply concepts of scale and proportion while learning about how electrospinning turns dough into nanonoodles.