Search Results
Cosmic Collision: A Far-Flung Possibility
Computer models suggest a remote yet haunting possibility— that passing stars could carry the potential to warp Earth’s orbit, triggering a cosmic collision. Answer questions about cause and effect. Discuss matter from the scale of the tiniest quark to the vastness of the known universe.
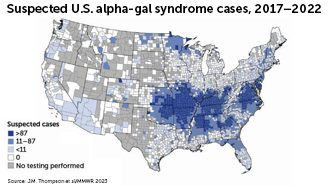
Mapping the spread of ticks
Three types of ticks may spread alpha-gal syndrome, an allergy to red meat. Researchers think the condition is caused by molecules in the saliva of certain tick species. The best way to avoid the syndrome is to prevent tick bites.

A Virtual Immune-Boost and Hybridization
Pair these lesson plans with articles from the October issue of Science News to review genetics concepts, explore natural and artificial selection and discuss the potential to virtually boost immune responses.
A virtual immune-boost
Exposure to germs triggers an immune response. But just thinking about germs might do it, too, new data show. Researchers used virtual reality to study how people respond to sickness in others. Learn techniques and tools researchers use to study how we respond to illness at three levels of biological organization — the behavioral, physiological and chemical. Answer questions about experimental variables, then discuss possible applications for virtually boosted vaccines of the future.
Hybrid hijinks
In this lesson, students will review genetics concepts, explore natural and artificial selection, and take a closer look at hybridization.
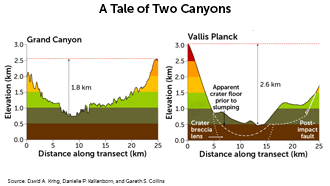
Lunar landforms
Researchers analyzed images of giant canyons on the moon to deduce the physics of how they formed. A massive impact 3.8 billion years ago shot out rock that plunged 3.5 kilometers into the lunar surface, carving two canyons in less than 10 minutes.
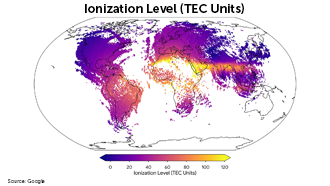
Using smartphone data to probe the ionosphere
A sea of charged particles swirls in the ionosphere, a layer at the edge of Earth’s atmosphere. Shifts in the ionosphere can muddle radio signals key for navigation systems. But pooling data from millions of phones equipped with GPS receivers could help fix errors caused by the meddlesome atmospheric layer.

A Squirrely Robot and Stinky Plants
Incorporate articles from the October issue of Science News Explores to learn how scientists used biomimicry to engineer a new type of robot and answer questions about the biological and chemical processes happening in plants that have evolved to increase their stench.
Here come the squirrel-bots
Inspired by nature’s greatest acrobats, roboticists have made engineering leaps — creating and upgrading an agile, jumping robot that can grasp branches like a squirrel. Learn how scientists use biomimicry to launch new approaches to old engineering challenges. At the same time, explore concepts of momentum in daily life, then answer questions about possible applications for squirrely robots of the future.
How plants level up their stink
Some plants have evolved to produce putrid scents. Consider the phenomenon of smell before doing a card sort to show the biological and chemical processes happening in these plants. Then, answer questions about why and how the plants evolved to increase their stench.

Sink or Swim: Exploring Bone Density and Buoyancy
Based on recent research, Spinosaurus is depicted swimming in the newest Jurassic World movie. Some studies point to Spinosaurus’s relatively dense bones, which could have helped control buoyancy for swimming. But others argue that Spinosaurus fossils point to its life as a wader.
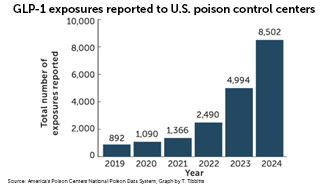
The weight of weight-loss drug usage
Shortages and big price tags have driven patients to unconventional, sometimes shady sources of weight-loss drugs. In some cases, people end up with tainted drugs or risk overdosing.