Search Results
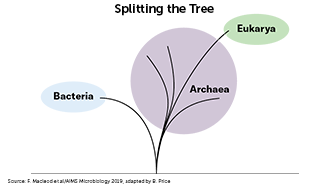
A look at life’s origins
A group of single-celled microbes that belong to the domain of life known as archaea may have been crucial to the evolution of complex life. Members of this group, known as Asgard archaea, seem to have evolved in several ways that primed them to give rise to multicellular life. This suggests that complex life may evolve more easily than biologists have thought, but researchers are still working out how exactly it could have happened.
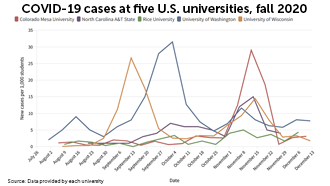
Dorm room data: COVID-19 cases in 5 universities
Universities that opened their campuses in fall 2021, during the COVID-19 pandemic, faced an uncharted, months-long experiment in infection control. Science News looked at the measures five universities took. Each school cobbled together periodic testing with rules about masks and public gatherings.
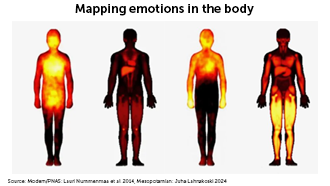
Mapping emotions in the body
For 3,000 years, humans have connected emotions to some of the same body parts. An analysis of clay tablets reveals that ancient Mesopotamians felt love in the heart and fear in the gut, as we do today.
Exercise and education
In this activity, students will design an experiment to observe how exercise affects their ability to concentrate in class. Students will then read the Science News Explores article “Short exercise workouts can boost classroom performance” and analyze how their experiment differed from the experiment described in the article.
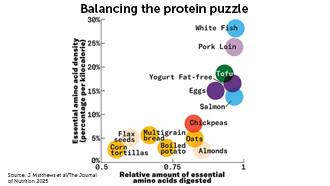
Balancing the protein puzzle
Protein is having a moment. It’s cropping up as an additive in all sorts of foods, and social media influencers tout high-protein diets as key to big muscles. But people in the United States typically get enough protein; they just might not be getting the right mix.

Eyes are not all equal
Golden apple snails can completely regrow a functional eye within months of having lost one. Understanding how the snails re-create or repair their eyes might someday lead to therapies to heal people’s eye injuries or reverse some eye diseases.
The brain provides answers
Brain scans can help scientists answer questions about how the brain receives information from parts of the body and controls them. In this short activity, students will think of a question that could potentially be answered by brain scans and write a scientific question.
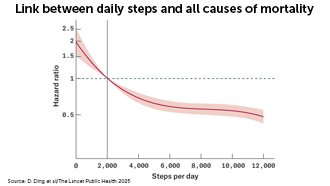
Take a hike
Walking just 7,000 steps per day can lower a person’s risk of certain health issues, according to a new study. Even a small increase in steps per day lowered health risks.
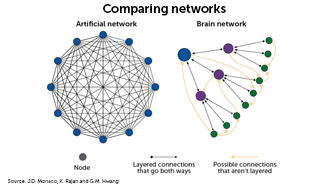
Wiring the mind
Researchers are drawing inspiration from the brains of creatures from worms to humans to develop more efficient, more capable forms of AI.
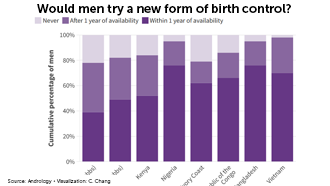
The rise of male contraceptive options
Contraceptive pills for women emerged in 1960, followed by hormonal implants, patches, vaginal rings and IUDs. But no new contraceptive methods have become available for men. New research could change that in the next five to 10 years.
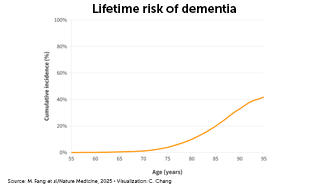
U.S. dementia cases on the rise
Scientists predict that, by 2060, one million U.S. adults per year will develop dementia. The new estimate surpasses previous estimates of how many people will struggle with memory, reasoning and language difficulties that interfere with life.
A virtual immune-boost
Exposure to germs triggers an immune response. But just thinking about germs might do it, too, new data show. Researchers used virtual reality to study how people respond to sickness in others. Learn techniques and tools researchers use to study how we respond to illness at three levels of biological organization — the behavioral, physiological and chemical. Answer questions about experimental variables, then discuss possible applications for virtually boosted vaccines of the future.