Tech
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Tech
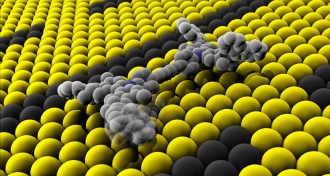
TechTiniest car gets a test drive
Scientists build the world's tiniest electric 'roadster,' and zap it into action.
-
 Tech
TechMining electronic records yields connections between diseases
Mining patient records, combined with molecular research, may reveal new links among medical conditions.
-

-
 Tech
TechEinstein invents automatic camera
Einstein invents fridges,cameras and clothing.
By Science News -
 Tech
TechGrowing need for space trash collectors
On April 2, for the fifth time in less than three years, the International Space Station fired its engines to dodge a piece of orbital debris that appeared on a collision path. Other spacecraft also regularly scoot out of the way of rocket and satellite debris. Such evasive action will be needed increasingly frequently, a new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
 Tech
TechSparing the rare earths
Potential shortages of useful metals inspire scientists to seek alternatives for magnet technologies
By Devin Powell -
 Tech
TechComputers get under our skin
Epidermal devices offer new potential to integrate electronics into the body.
-
 Tech
TechCracked sewers bleed fecal germs
Studies follow leaks into waterways and drinking supplies.
By Janet Raloff -
 Tech
TechAirports’ leaden fallout may taint some kids
People who live below the flight path of piston-engine aircraft — or downwind of airports serving such small planes — are exposed to lead from aviation fuel. A new study now links an airport’s proximity to somewhat elevated blood-lead levels in children from area homes.
By Janet Raloff -
 Tech
TechSome comfort about broken CFLs
My night-owl daughter woke me in a panic at around 2 a.m., a couple of weeks back. While swatting at a fly, she’d just broken the compact fluorescent light illuminating her closet. Having heard me warn endlessly of how we should be careful in handling these bulbs — since they contain mercury — she wanted to know what kind of damage control was called for. I only wish I knew then what I do now.
By Janet Raloff -
 Tech
TechBatteries not included
Researchers have developed a sensor that, when flexed, generates enough charge to send wireless signals.
-
 Tech
TechNew technique spins superlong nanowires
Made from any number of materials, fibers are millionths of a millimeter across and kilometers long.