Space
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Planetary Science
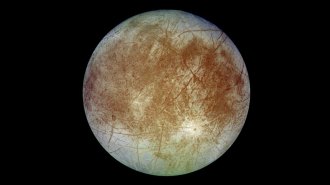
Planetary ScienceEuropa may have much more shallow liquid water than scientists thought
Mysterious pairs of ridges scar Jupiter’s moon Europa. Analyzing a similar set in Greenland suggests shallow water is behind the features’ formation.
By Sid Perkins -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHere’s how NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter has spent 1 year on Mars
The first flying robot on the Red Planet arrived as a technology demonstration. It’s now a trusty scout for its rover partner, Perseverance.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyCrumbling planets might trigger repeating fast radio bursts
Mysterious blasts of cosmic radio waves might be due to planets sweeping extremely close to their host neutron stars.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA newly discovered planet renews debate about how some giant worlds form
An implosion of gas may have given birth to this young exoplanet, which orbits too far from its star to have been built up bit by bit, researchers say.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThis is the biggest known comet in our solar system
The nucleus of comet Bernardinelli-Bernstein is about 120 kilometers across — about twice the width of Rhode Island — and is darker than coal.
By Sid Perkins -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNew thermal maps of Neptune reveal surprising temperature swings
Neptune's atmospheric temperatures show a global drop and later, a weird isolated spike at the south pole. Scientists don't yet know why.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars has two speeds of sound
High-pitched clacks from a laser on NASA’s Perseverance rover zapping rocks traveled faster than the lower-pitched hum of the Ingenuity helicopter’s blades.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA star nicknamed ‘Earendel’ may be the most distant yet seen
Analyzing Hubble Space Telescope images revealed a star whose light originates from about 12.9 billion light-years away, researchers say.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Space
SpaceBinary stars keep masquerading as black holes
The drive to find black holes in ever-larger astronomy datasets is leading some researchers astray.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhen the Magellanic Clouds cozy up to each other, stars are born
The Magellanic Clouds, the two closest star-making galaxies to the Milky Way, owe much of their stellar creativity to each other.
By Ken Croswell -
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s the best timeline yet for the Milky Way’s big events
A new study puts more precise dates on when the Milky Way formed its thick disk and collided with a neighboring galaxy.
By Ken Croswell -
 Physics
PhysicsLevitating plastic beads mimic the physics of spinning asteroids
"Tabletop asteroids," buoyed by sound waves, hint at why some loosely bound space rocks have odd shapes and can’t spin too quickly.