Space
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Planetary Science
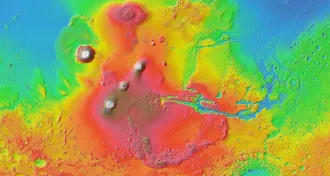
Planetary ScienceRed Planet’s interior may not churn much
The magma fueling a Martian volcanic system remained largely unchanged for billions of years, analysis of a newfound meteorite suggests.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySpin may reveal black hole history
High rate of spin could indicate that black holes formed from previous mergers of black holes.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceOxygen atoms from Earth bombard the moon
Oxygen atoms originating from the upper atmosphere periodically bombard the moon’s surface, researchers propose.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPossible sign of dark matter shows up again
Excess of X-rays could indicate decaying sterile neutrinos.
-
 Astronomy
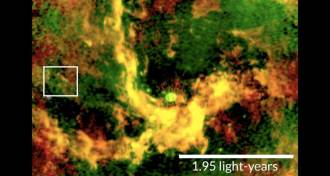
AstronomyConditions right for stars, planets near Milky Way’s supermassive black hole
Four clouds of gas near the galactic center have roughly the right mass to be young stars, possibly with planets.
-
 Animals
AnimalsReaders weigh in on mathematical animals and more
Animal math, dinosaur digestion and more in reader feedback from our December 10, 2017, issue.
-
 Life
LifeAsteroid barrage, ancient marine life boom not linked
Impacts from asteroid debris probably didn’t trigger the boom in marine animal diversity around 471 million years ago during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event.
-
 Planetary Science
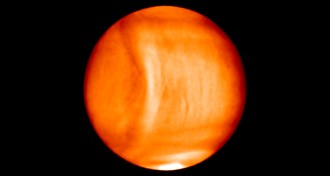
Planetary ScienceWeird wave found in Venus’ wind-whipped atmosphere
A 10,000-kilometer-long gravity wave arched across the upper atmosphere of Venus. The feature may have been the largest of its kind in the solar system.
-
 Climate
ClimatePetrified tree rings tell ancient tale of sun’s behavior
The 11-year cycle of solar activity may have been around for at least 290 million years, ancient tree rings suggest.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe moon is still old
New analysis of moon rocks points to our satellite forming about 4.51 billion years ago, roughly 60 million years after the start of the solar system.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMilky Way’s black hole may hurl galactic spitballs our way
Gas blobs formed in the wake of stars shredded by the black hole in the center of the galaxy could pass within several hundred light-years of Earth on their way to intergalactic space.
-
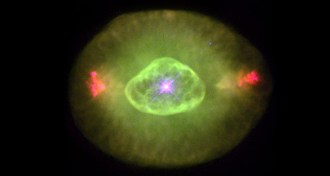 Astronomy
AstronomyEarliest galaxies got the green light
Galaxies in the early universe might have emitted lots of green light, powered by large populations of stars much hotter than most found today.