Plants
-
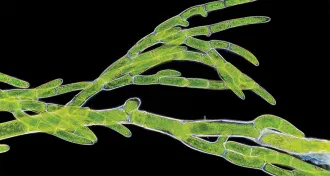 Plants
Plants‘Slime’ shows how algae have shaped our climate, evolution and daily lives
The new book ‘Slime’ makes the case that algae deserve to be celebrated.
-
 Life
Life‘Sneezing’ plants may spread pathogens to their neighbors
A “surface tension catapult” can fling dewdrops carrying fungal spores from water-repellent leaves.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPeople may have smoked marijuana in rituals 2,500 years ago in western China
Cannabis may have been altering minds at an ancient high-altitude cemetery, researchers say
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeSome fungi trade phosphorus with plants like savvy stockbrokers
New views show how fungi shift their stores of phosphorus toward more favorable markets where the nutrient is scarce.
By Susan Milius -
 Environment
EnvironmentHow one fern hoards toxic arsenic in its fronds and doesn’t die
To survive high levels of arsenic, a fern sequesters the heavy metal in its shoots with the help of three proteins.
-
 Plants
PlantsSome plants use hairy roots and acid to access nutrients in rock
Shrubs in mountainous areas of Brazil have specialized roots that secrete chemicals to extract phosphorus from rock.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow allergens in pollen help plants do more than make you sneeze
A plant’s view of what humans call allergens in pollen grains involves a lot of crucial biology. And sex.
By Susan Milius -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAn ancient pouch reveals the hallucinogen stash of an Andes shaman
South American shamans in the Andes Mountains carried mind-altering ingredients 1,000 years ago, a study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateClimate change made the Arctic greener. Now parts of it are turning brown.
Arctic browning could have far-reaching consequences for people and wildlife, affecting habitat and atmospheric carbon uptake as well as increasing wildfire risk.
By Hannah Hoag -
 Plants
PlantsA major crop pest can make tomato plants lie to their neighbors
Insects called silverleaf whiteflies exploit tomatoes’ ability to detect damage caused to nearby plants.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyReaders have questions about Ultima Thule, thirsty plants and vitamin D
Readers had comments and questions about Ultima Thule, photosynthesis and more.
-
 Plants
PlantsShutdown aside, Joshua trees live an odd life
Growing only in the U.S. Southwest, wild Joshua trees evolved a rare, fussy pollination scheme.
By Susan Milius