Planetary Science
-
 Space
SpaceMoonquakes are much more common than thought, Apollo data suggest
The discovery of 22,000 previously unseen moonquakes, plus a new idea of what causes them, could help us better prepare for trips there.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s Perseverance rover finds its first possible hint of ancient life on Mars
The NASA Mars rover examined a rock containing organic compounds and “leopard spots” that, on Earth, are associated with microbial life.
-
 Space
SpaceA planet needs to start with a lot of water to become like Earth
Rocky planets around fiery stars could hide their water for later use, but it takes 3 to 8 times the amount in our world’s oceans to end up Earthlike.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s Great Red Spot may be less than 200 years old
An analysis of images spanning hundreds of years suggests a dark spot spied in the late 1600s and early 1700s is distinct from the Red Spot seen today.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSulfur was key to the first water on Earth
Hydrogen bonded with sulfur may have given our world its first water after the hydrogen broke away and joined with oxygen in the planet’s crust.
By Ken Croswell -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceVenus might be as volcanically active as Earth
Data from NASA’s Magellan spacecraft suggest that volcanic activity is widespread on Venus.
By Adam Mann -
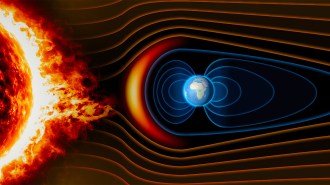 Earth
EarthA weaker magnetic field may have paved the way for marine life to go big
Decreased protection from cosmic radiation may have increased oxygen levels in the atmosphere and oceans, allowing animals to grow larger.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePluto’s heart-shaped basin might not hide an ocean after all
Planetary scientists propose an alternative theory to explain why Sputnik Planitia has stayed put across Pluto’s equator.
By Adam Mann -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceOur picture of habitability on Europa, a top contender for hosting life, is changing
The moon of Jupiter is considered one of the most promising places to look for life, but its subsurface ocean may be less habitable than once thought.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s moon Io may have been volcanically active ever since it was born
An analysis of the moon’s atmospheric composition suggests that it has been spewing sulfur for roughly 4.6 billion years.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTitan’s dark dunes could be made from comets
Saturn’s largest moon could have gotten its sands from an ancient reshuffling of the solar system. If true, that would solve a long-standing mystery.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe desert planet in ‘Dune’ is plausible, according to science
Humans could live on the fictional planet Arrakis from Dune but (thankfully) no giant sandworms would menace them.