Planetary Science
-
 Space
SpaceHayabusa2’s asteroid dirt may hold clues to the early solar system
“We collected the treasure box,” a Japanese space scientist announced after a capsule holding samples from asteroid Ryugu safely landed on Earth.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary Science50 years ago, scientists caught their first glimpse of amino acids from outer space
In 1970, scientists detected amino acids in a meteorite. Fifty years later, a variety of chemical ingredients for life have been found in other space rocks.
-
 Space
SpaceDecember’s stunning Geminid meteor shower is born from a humble asteroid
Most meteor showers arise from comets, but the robust Geminid shower comes from an asteroid, Phaethon, which scientists are still trying to figure out.
By Ken Croswell -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChina is about to collect the first moon rocks since the 1970s
The robotic Chang’e-5 mission, which landed on an unexplored region of the moon December 1, aims to gather samples and return them to Earth.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFarming on Mars will be a lot harder than ‘The Martian’ made it seem
Lab experiments developing and testing fake Martian dirt are proving just how difficult it would be to farm on the Red Planet.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChemical reactions high in Mars’ atmosphere rip apart water molecules
Mars is so dry because its water constant escapes into space. A new study suggests this process occurs in the ionosphere and faster than thought.
-
 Space
SpaceJupiter’s icy moon Europa may glow in the dark
Europa’s potential “ice glow” could help scientists map the chemical composition of its surface — and the ocean underneath.
-
 Space
SpaceJupiter may host atmospheric ‘sprites’ or ‘elves’ never seen beyond Earth
For the first time, NASA’s Juno spacecraft may have spied the bright, superfast light show on another world.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceDoubts over a ‘possible sign of life’ on Venus show how science works
Detecting phosphine in Venus’ atmosphere made headlines, but reanalyses and new searches call into question the original discovery of the molecule.
-
 Space
SpaceWater exists on sunny parts of the moon, scientists confirm
New observations of the moon, made by a telescope flying onboard a Boeing 747-SP jet, have confirmed the presence of water on sunlit areas of the moon.
-
 Space
SpaceNASA’s OSIRIS-REx survived its risky mission to grab a piece of an asteroid
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft just tried to grab a piece of asteroid Bennu. If successful, the spacecraft will return the sample to Earth in 2023.
-
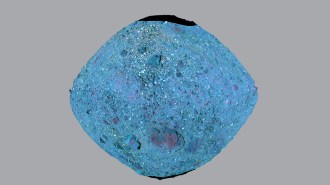 Space
SpaceThe asteroid Bennu’s brittle boulders may make grabbing a sample easier
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is about to collect a bit of asteroid Bennu. Here’s why it’s good that new research suggests its boulders are brittle.