Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Materials Science
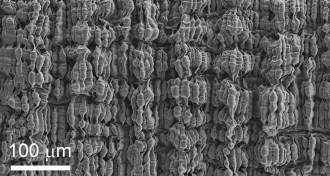
Materials ScienceStretchy fiber lets electrons flow
Folded layers of carbon nanotubes allow an elastic fiber to conduct electrical current when stretched.
By Andrew Grant -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceStretchy fiber keeps electrons flowing
Folded layers of carbon nanotubes allow an elastic fiber to conduct electrical current when stretched.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsElusive particle shows up in ‘semimetal’
Weyl fermions, which resemble massless electrons, have been spotted inside tantalum arsenide. Their discovery comes 86 years after they were proposed.
By Andrew Grant -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsLHC reports pentaquark sightings
Two particles discovered at the Large Hadron Collider are composed of five quarks, not two or three like nearly every other known quark-based particle.
By Andrew Grant -
 Astronomy
AstronomySource of blazars’ super brightness comes into focus
Astronomers take a close look at a blazar, a galaxy whose central black hole emits gamma rays and other high-energy material toward Earth.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
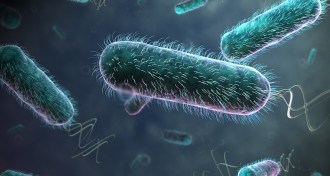
PhysicsSwimming bacteria remove resistance to flow
The collective motion of swimming bacteria can virtually eliminate a water-based solution’s resistance to flow.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsThe arrow of time
Gravity may explain how time always runs forward, even though the laws of physics should permit it to run backward.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsMagnetic test boosts case for record-setting superconductor
New measurements bolster the case that hydrogen sulfide is superconducting at about 200 kelvins, roughly 40 kelvins higher than any other known material.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
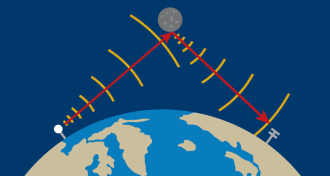
PhysicsIn retirement, Nobelist takes up moon bouncing
A lifelong amateur radio enthusiast, Joseph Taylor sends signals via the moon.
By Julia Rosen -
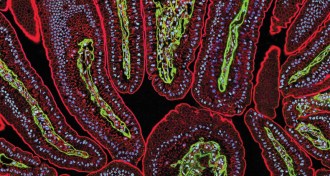 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum dots get a second chance to shine
Quantum dots, semiconductor particles that can emit a rainbow of colors, have been put to work observing living cells, with possible benefits for medical diagnosis.
-
 Physics
Physics‘The Science of TV’s the Big Bang Theory’ educates as it entertains
A science book inspired by fictional scientists helps readers understand everything from particle physics to potato electricity.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyDeflategate favored foul play over science
Science didn’t get center stage in the rulings on whether the New England Patriots underinflated footballs during championship game against the Indianapolis Colts.