Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Physics
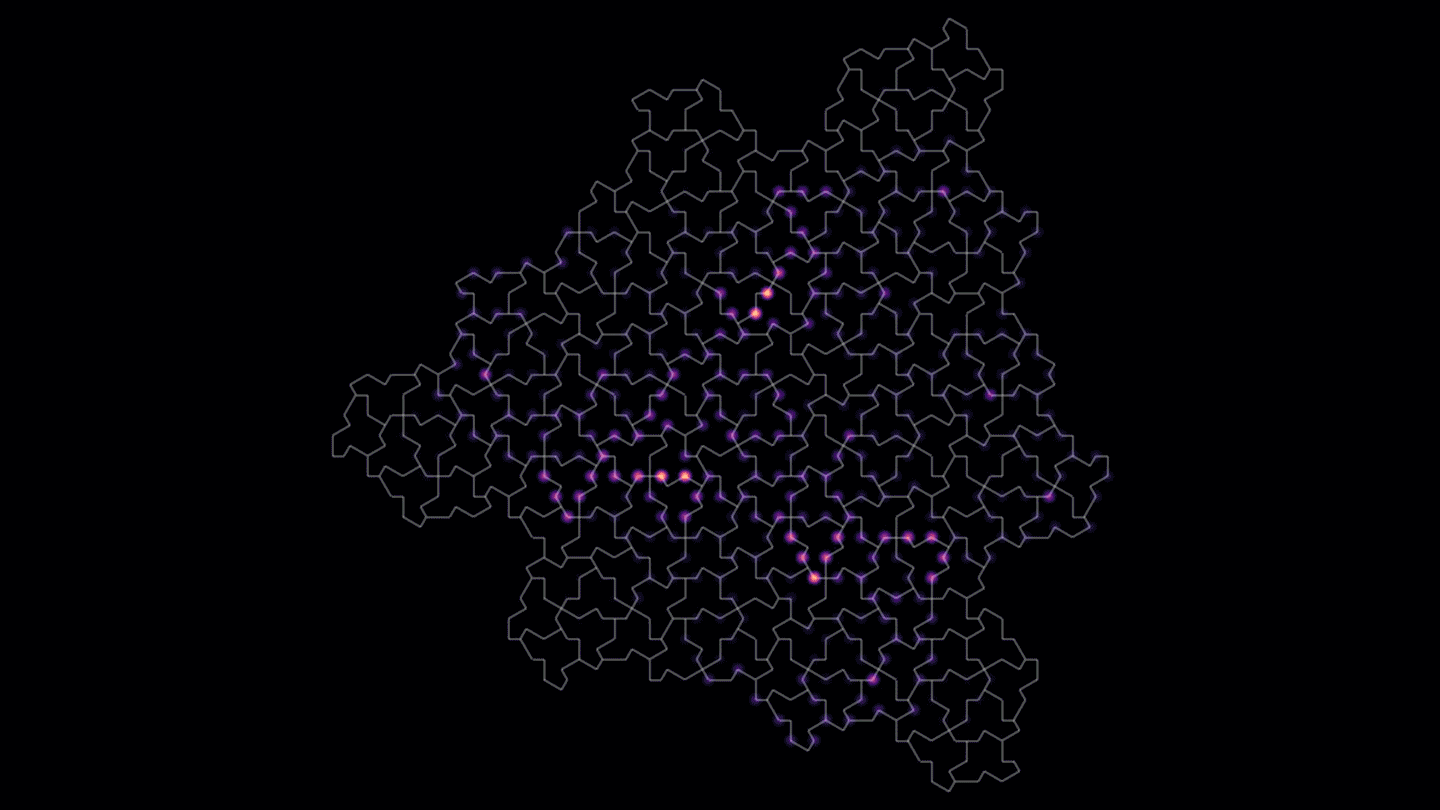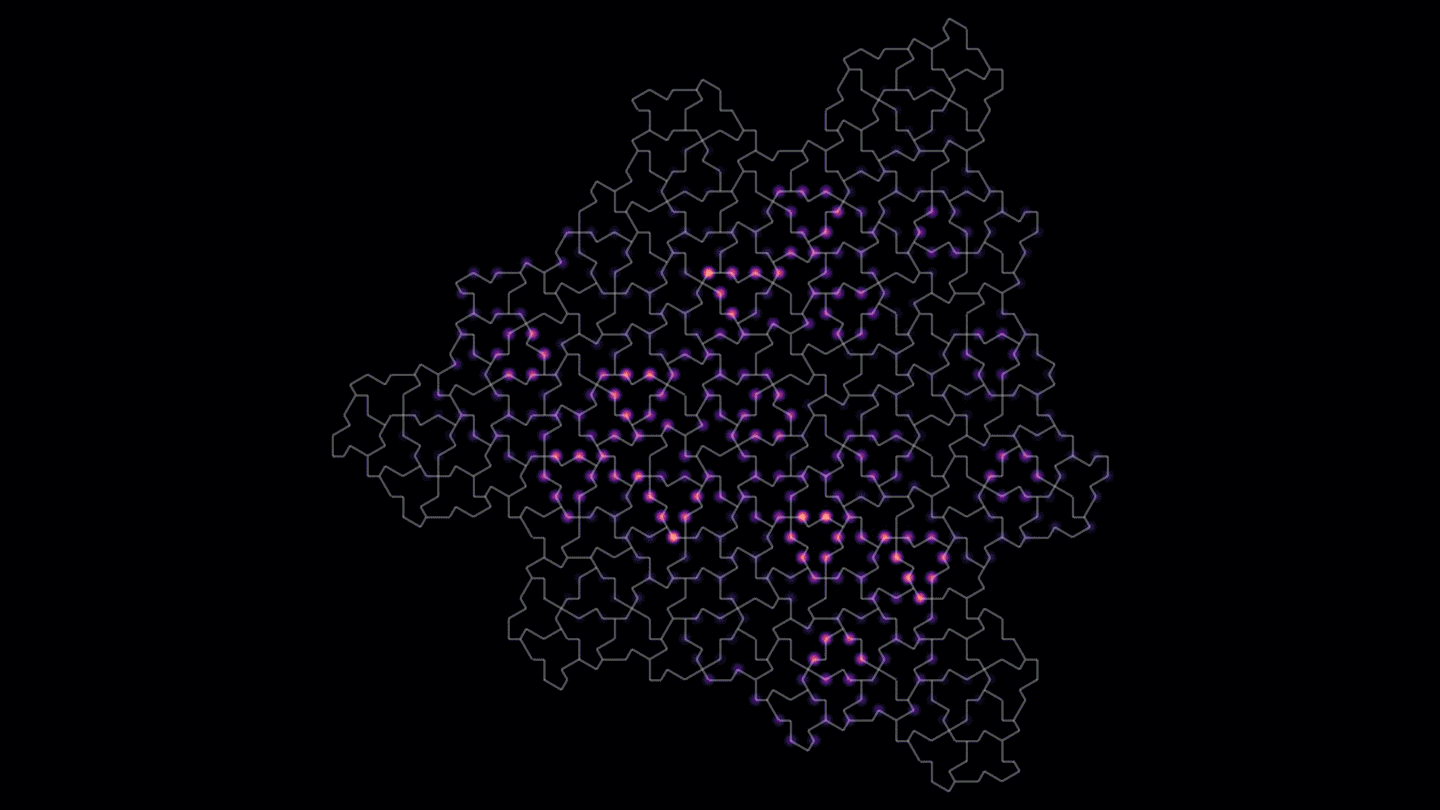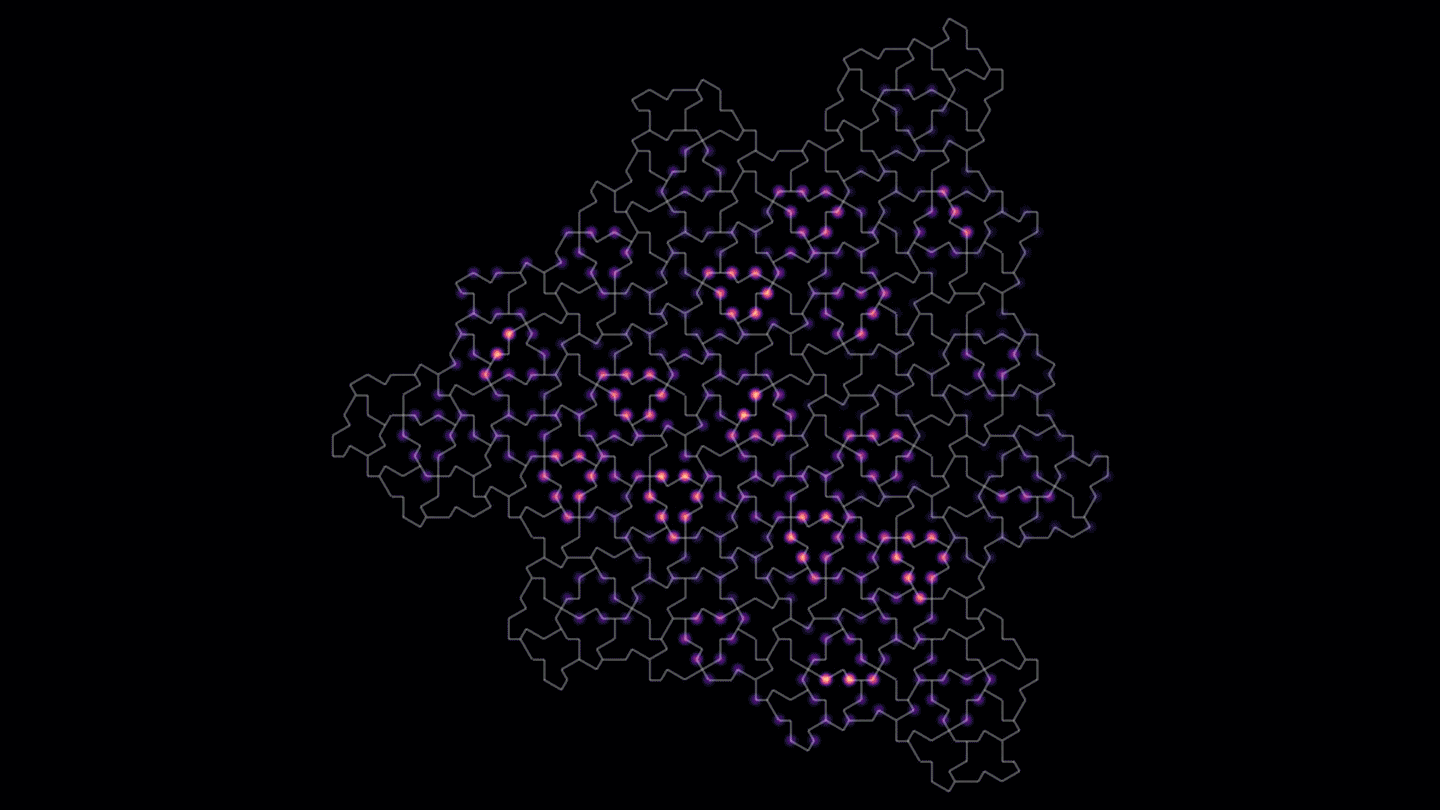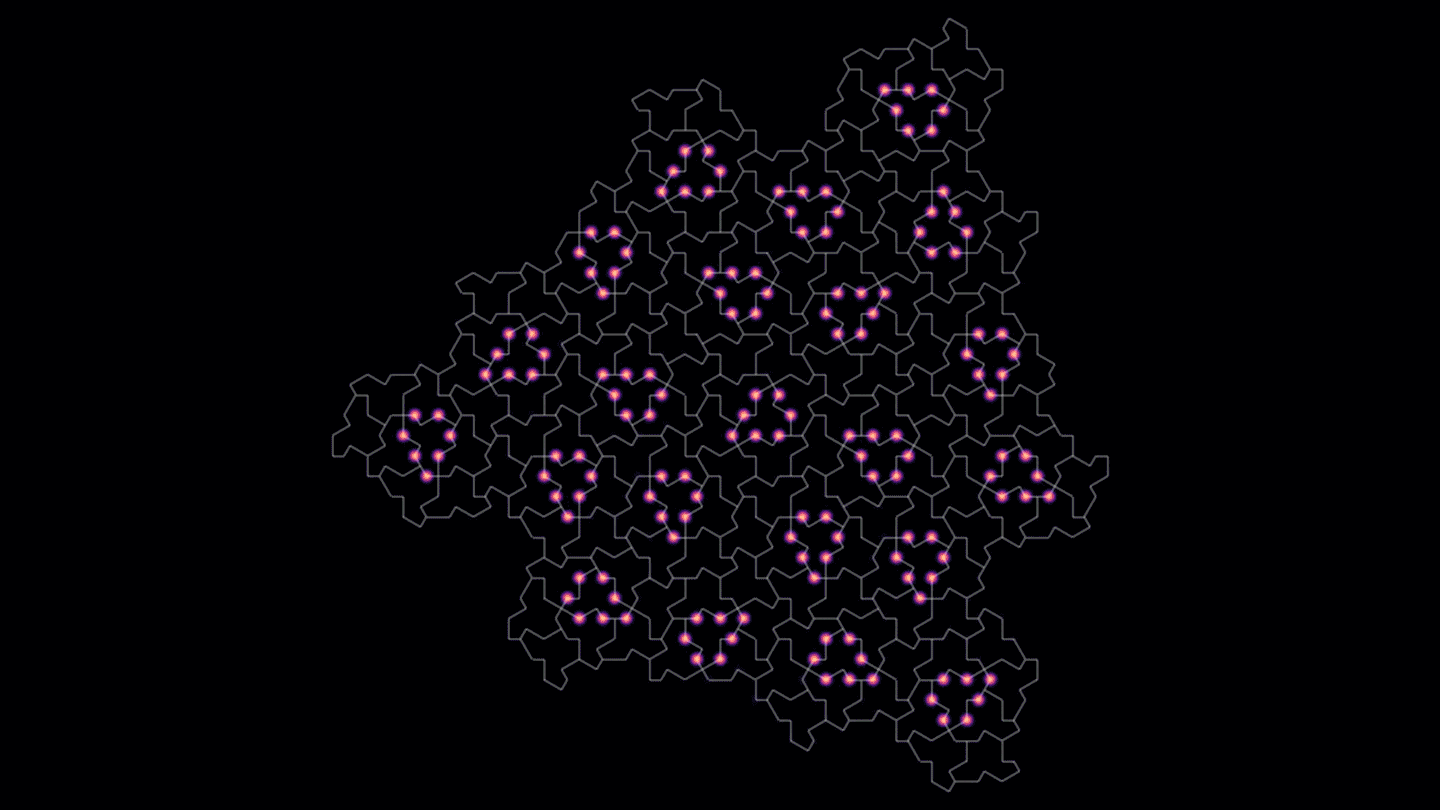
PhysicsA predicted quasicrystal is based on the ‘einstein’ tile known as the hat
The einstein tile can cover an infinite plane only with a nonrepeating pattern. A material based on it has features of both crystals and quasicrystals.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWhat happens when lawn sprinklers suck in water? Physicists answer that quirky question
Experiments with a floating sprinkler and laser-illuminated microparticles revealed the surprisingly complex physics behind a simple question.
-
 Physics
Physics50 years ago, timekeepers deployed the newly invented leap second
After more than 50 years, metrologists will stop using the leap second to align the time kept by atomic clocks with the rate of Earth’s spin.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceArtificial intelligence helped scientists create a new type of battery
It took just 80 hours, rather than decades, to identify a potential new solid electrolyte using a combination of supercomputing and AI.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA fiber inspired by polar bears traps heat as well as down feathers do
Scientists took a cue from polar bear fur to turn an ultralight insulating material into knittable thread.
By Jude Coleman -
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s the science behind the burbling sound of water being poured
The height of the pour and the thickness of the stream help determine the loudness of the falling water.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s how much fruit you can take from a display before it collapses
About 10 percent of the fruit in a tilted market display can be removed before it all crashes down, computer simulations show.
-
 Earth
EarthSTEVE and other aurora-like glows perplex scientists with their complex physics
New views of STEVE from citizen scientists keep raising questions about the atmospheric light show — but computer models may offer some answers.
-
 Physics
PhysicsInvisible comet tails of mucus slow sinking flakes of ‘marine snow’
New measurements reveal the gunk that surrounds the particles, an important factor in understanding how the ocean sequesters carbon.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA maverick physicist is building a case for scrapping quantum gravity
To merge quantum physics and general relativity, physicists aim to quantize gravity. But what if gravity isn’t quantum at all?
-
 Earth
EarthBefore ancient Egyptians, nature sculpted sphinxes. Here’s how
Steady winds can carve landforms called yardangs — thought to have inspired the Great Sphinx of Gaza — from featureless blobs, a new study suggests.
By Elise Cutts -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA rare, extremely energetic cosmic ray has mysterious origins
In 1991, physicists spotted a cosmic ray with so much energy it warranted an ‘OMG.’ Now that energetic particle has a new companion.