Neuroscience
-
 Tech
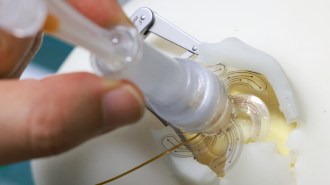
TechA flower-shaped soft robot could make brain monitoring less invasive
Once inserted in the skull, the device unfurls flexible sensors that can monitor the brain's electrical activity less invasively than current methods.
By Bob Hirshon -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists decoded people’s thoughts using brain scans
The finding may lead to better communication aids for people who can’t communicate easily. It also raises privacy concerns.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe classic map of how the human brain manages movement gets an update
Functional MRI scans provide a new version of the motor homunculus, the mapping of how the primary motor cortex controls parts of the body.
-
 Neuroscience
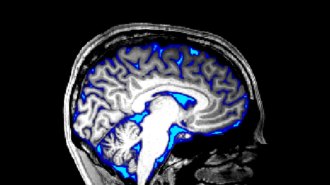
NeuroscienceScientists triggered the flow of spinal fluid in the awake brain
If future studies confirm these waking waves wash away toxic proteins from the brain, the finding could lead to new treatments for brain disorders.
By Simon Makin -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYour brain wires itself to match your native language
MRI scans of nearly 100 native speakers of either German or Arabic revealed differences in how the language circuits of their brains are connected.
By Elise Cutts -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists have now recorded brain waves from freely moving octopuses
The data reveal some unexpected patterns, though it’s too early to know how octopus brains control the animals’ behavior, a new study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIn mice, anxiety isn’t all in the head. It can start in the heart
Scientists used optogenetics to raise the heartbeat of a mouse, making it anxious. The finding could offer a new angle for studying anxiety disorders.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceScientists have mapped an insect brain in greater detail than ever before
Researchers have built a nerve cell “connectivity map” of a larval fruit fly brain. It’s the most complex whole brain wiring diagram yet made.
-
 Life
Life‘We Are Electric’ delivers the shocking story of bioelectricity
Sally Adee’s new book spotlights the underexplored science of the body’s electricity and investigates how bioelectricity could advance medicine.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow meningitis-causing bacteria invade the brain
Microbes behind bacterial meningitis hijack pain-sensing nerve cells in the brain’s outer layers, disabling a key immune response, a mouse study shows.
-
 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Mommy brain’ doesn’t capture how the brain transforms during pregnancy
During the transition to motherhood, there's more going on than “momnesia,” neuroscientists argue. The brain changes to prep for the job of caregiving
-
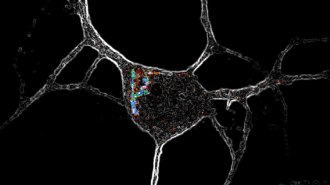 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePsychedelics may improve mental health by getting inside nerve cells
Psychedelics can get inside neurons, causing them to grow. This might underlie the drugs’ potential in combatting mental health disorders.