Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMapping aggression circuits in the brain
Using optogenetics and other techniques, scientists are tracing connections to and from the brain’s aggression command center.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Neuroscience
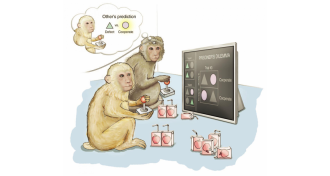
NeuroscienceBrain cells predict opponent’s move in game-playing monkeys
Newly discovered brain cells help monkeys predict whether a companion will cooperate.
-
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBees may merge their flower memories
Bumblebees sometimes prefer fake flowers with the combined patterns and colors of ones seen before, suggesting they merge memories of past experiences.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBlame pot munchies on nerve cells that normally nix appetite
Pot munchies demystified: Marijuana hijacks fullness nerve cells, making them send hunger signals instead.
-
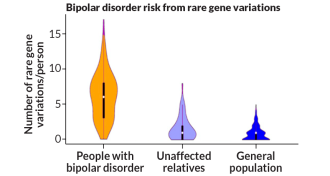 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBipolar risk boosted by accumulation of rare versions of genes
A buildup of rare versions of genes that control nerve cell activity contributes to the genetic risk of bipolar disorder.
-
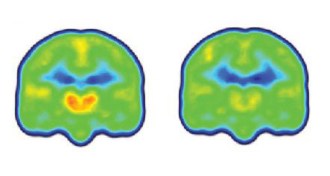 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChronic pain treatments may get boost from high-tech imaging
Advanced imaging may reveal how well chronic pain treatments work.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen you’re happy and you show it, dogs know it
A new test using pictures of halves of human faces challenges dogs’ abilities to read people’s emotions.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGlowing amino acid lights up growing brain cancer
By adding a tracer compound that sticks to the amino acid glutamine, researchers may be able to discern and monitor cancerous tissues in the brain.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyFinding joy and inspiration in the pursuit of knowledge
Editor in Chief Eva Emerson ruminates on the power of knowledge, and the ways scientists are refining how we think about the aging human brain, far away comets and even the speed of light.
By Eva Emerson -
 Psychology
PsychologyAdults with autism are left to navigate a jarring world
Researchers are beginning to study ways to help adults with autism navigate independently, get jobs and find friendship.
-
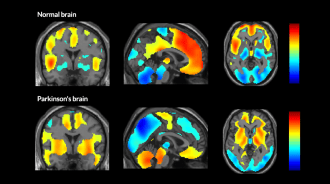 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA brain at rest offers clues to Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s
PET scans reveal that the breakdown of brain networks differs in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.