Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
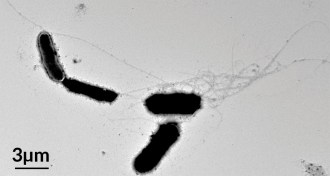
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s culprit may fight other diseases
A notorious Alzheimer’s villain may help bust microbes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWiping out gut bacteria impairs brain
Antibiotics that wiped out gut bacteria curbed brain cell production in mice, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMath offers new view of brain and its disorders
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses new insights into the brain's role in mental illness, sleep, and ancient rituals.
By Eva Emerson -
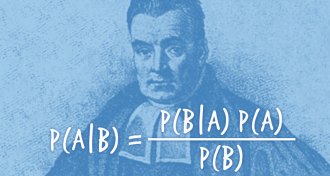 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBayesian reasoning implicated in some mental disorders
An 18th century math theory may offer new ways to understand schizophrenia, autism, anxiety and depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves in REM sleep help store memories
Mice with disturbed REM sleep show memory trouble.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSocial area of the brain sets threat level of animals
How people perceive an animal’s danger level is encoded in a particular wrinkle of cortex, a brain scan study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA breakdown product, not ketamine, may ease depression
Ketamine’s breakdown product, not the drug itself, eases depression, a mouse study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
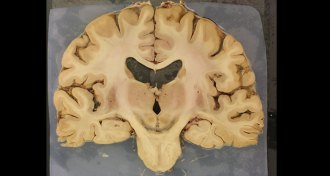
NeuroscienceEvidence conflicts on iron’s role in Parkinson’s disease
Experiments yield conflicting results about whether vulnerable nerve cells have too much or too little iron.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDragons sleep like mammals and birds
Some lizards may sleep in the same way as mammals and birds, a new brain wave study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIons may be in charge of when you sleep and wake
The recipe for sleep and wake may depend on ions.
-
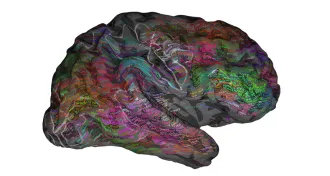 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWords’ meanings mapped in the brain
Language isn’t just confined to one region of the brain: The meaning of words spark activity all over the cerebral cortex.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFindings on wobbly memories questioned
In contrast to older studies, new results suggest that new memories don’t interfere with older, similar ones.