Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
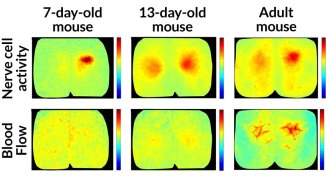
NeuroscienceNewborn brain has to learn how to feed itself
Nerve cells in newborn mice can’t yet feed themselves.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCocaine addicts can’t kick other habits either
Habitual users tend to get stuck in nondrug-related habits more easily, too, pointing to a potential strategy for treatment
-
-
 Neuroscience
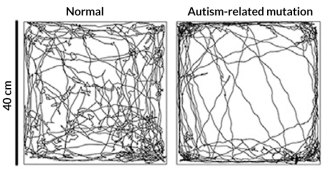
NeuroscienceAbnormal sense of touch may play role in autism
Autism-related genes are important for touch perception, a sense that may help the brain develop normally, a study of mice suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMorphine may make pain last longer
Instead of busting pain, morphine lengthened the duration of pain in rats with a nerve injury.
-
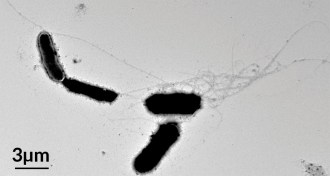 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s culprit may fight other diseases
A notorious Alzheimer’s villain may help bust microbes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWiping out gut bacteria impairs brain
Antibiotics that wiped out gut bacteria curbed brain cell production in mice, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMath offers new view of brain and its disorders
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses new insights into the brain's role in mental illness, sleep, and ancient rituals.
By Eva Emerson -
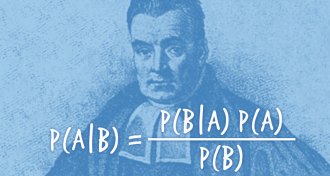 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBayesian reasoning implicated in some mental disorders
An 18th century math theory may offer new ways to understand schizophrenia, autism, anxiety and depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves in REM sleep help store memories
Mice with disturbed REM sleep show memory trouble.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSocial area of the brain sets threat level of animals
How people perceive an animal’s danger level is encoded in a particular wrinkle of cortex, a brain scan study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA breakdown product, not ketamine, may ease depression
Ketamine’s breakdown product, not the drug itself, eases depression, a mouse study suggests.