Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShape-shifting molecule aids memory in fruit flies
A prionlike protein may store long-term memories in fruit flies, a new study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEyes offer window into brain’s timekeepers
In new experiments of time perception, when pupils were large, monkeys underestimated a second.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFrequent liars show less activity in key brain structure
Brain activity changed as people lied more, a new study finds.
-
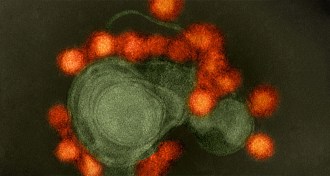 Genetics
GeneticsZika disrupts cellular processes to impair brain development
Discoveries about how Zika virus slows brain cell development could lead to treatments.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice smell, share each other’s pain
Pain can jump from one mouse to another, presumably through chemicals detected by the nose.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMelatonin makes midshipman fish sing
Melatonin lets people sleep but starts male midshipman fish melodiously humming their hearts out.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOut-of-sync body clock causes more woes than sleepiness
The ailment, called circadian-time sickness, can be described with Bayesian math, scientists propose.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBe careful what you say around jumping spiders
Sensitive leg hairs may let jumping spiders hear sounds through the air at much greater distances than researchers imagined.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsBees take longer to learn floral odors polluted by vehicle fumes
Car and truck exhaust mingling with a floral scent can slow down the important process of honeybees learning the fragrance of a flower.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNerve cell migration after birth may explain infant brain’s flexibility
A large group of neurons migrates into babies’ frontal lobes after birth.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPrimitive signs of emotions spotted in sugar-buzzed bumblebees
When bumblebees eat a sugary snack, they make more optimistic decisions, a new study finds. This could be early evidence for emotion in insects.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceJessica Cantlon seeks the origins of numerical thinking
Cognitive neuroscientist Jessica Cantlon wants to find out how humans understand numbers and where that understanding comes from.