Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice with a mutation linked to autism affect their littermates’ behavior
Genetically normal littermates of mutated mice behave strangely, suggesting that the social environment plays a big role in behavior.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMost football players who donated their brains to science had traumatic injury
A self-selected sample of 202 deceased football players, the largest to date, finds that the majority suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThere’s a long way to go in understanding the brain
Neuroscientists offer multiple “perspectives” on how to plug gaps in current knowledge of the brain’s inner workings.
-
 Animals
AnimalsRavens pass tests of planning ahead in unnatural tasks
Clever birds may have evolved their own broad powers of apelike thinking about the future.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain activity helps build an alpha male
In mice, nerve cells in the prefrontal cortex influence whether an individual is dominant or submissive.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceJust one night of poor sleep can boost Alzheimer’s proteins
Deep sleep may prevent the buildup of Alzheimer’s proteins.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains encode faces piece by piece
Cells in monkey brains build up faces by coding for different characteristics.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceObscure brain region linked to feeding frenzy in mice
Nerve cells in a little-studied part of the brain exert a powerful effect on eating, a mouse study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceInternal compass guides fruit fly navigation
Experiments show how flies navigate — and why this might be important for humans.
By Laura Beil -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA baby’s pain registers in the brain
EEG recordings can help indicate whether a newborn baby is in pain, a preliminary study suggests.
-
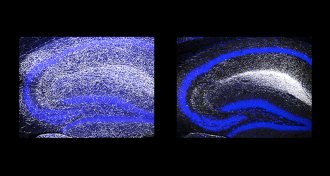 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNerve cell miswiring linked to depression
A gene helps nerve cell axons extend to parts of the brain to deliver serotonin, a brain chemical associated with depression.
-
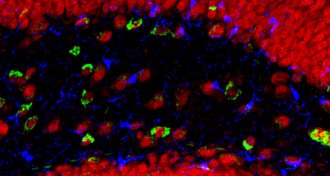 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain gains seen in elderly mice injected with human umbilical cord plasma
Plasma from human umbilical cord blood refreshes aspects of learning and memory in mice.