Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLoneliness is bad for brains
Social isolation shrinks nerve cells in the brains of mice, a new study shows.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyScreen time to heal, and perhaps to harm
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute reflects on the advances in virtual reality technology and how much time we spend on our computers and smartphones.
By Nancy Shute -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStimulating the spinal cord helps 3 more paralyzed people walk
There’s more evidence that with targeted spinal cord stimulation, paralyzed people can move voluntarily — and even walk.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYoung people’s memories improved when they stopped using marijuana
After just a week of not using pot, teens’ and young adults’ abilities to remember lists of words got better, a small study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMessing with fruit flies’ gut bacteria turns them into speed walkers
Without the right gut microbes, fruit flies walk faster and take shorter rests, results that highlight a new connection between the gut and brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTo unravel autism’s mysteries, one neuroscientist looks at the developing brain
Autism researcher Kevin Pelphrey focuses on understanding signs of the disorder in the developing brain, which could shed light on the condition.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePeople who have a good sense of smell are also good navigators
A sense of smell and a sense of direction are tangled in the brain, a new study finds.
-
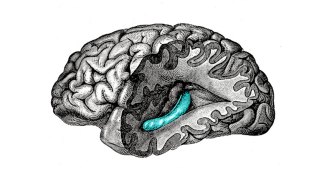 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow your brain is like a film editor
A brain structure called the hippocampus may slice our continuous existence into discrete chunks that can be stored as memories.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSurvey raises worries about how screen time affects kids’ brains
A large study of U.S. children ties lots of screen time to lower thinking skills, but the relationship between the two is still unclear.
-
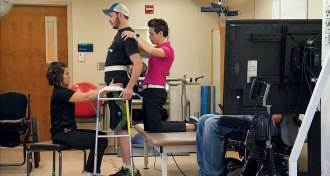 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA paralyzed man makes great strides with spinal stimulation and rehab
Researchers find success at restoring movement to paralyzed legs, giving hope to people with paraplegia.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOver-the-hill cells may cause trouble in the aging brain
Killing dormant cells in the brains of mice staved off memory trouble.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain features may reveal if placebo pills could treat chronic pain
Researchers narrow in on how to identify people who find placebos effective for treating persistent pain.