Neuroscience
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA single sweaty workout may boost some people’s memory
Memory improvements after a short bout of exercise mirrored those seen after months of training.
-
 Health & Medicine
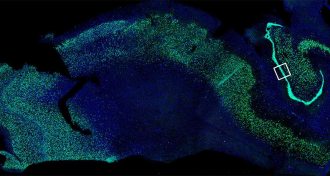
Health & MedicineSigns of new nerve cells spotted in adult brains
A study finds new evidence that adult brains grow new nerve cells, even the brain of an octogenarian.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWomen have a new weapon against postpartum depression, but it’s costly
The newly approved drug brexanolone simulates a natural hormone to alleviate symptoms of postpartum depression.
By Jeremy Rehm -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new ketamine-based antidepressant raises hope — and questions
Little is known about the long-term effects on people of a newly approved antidepressant based on the anesthetic ketamine.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePeople can sense Earth’s magnetic field, brain waves suggest
An analysis of brain waves offers new evidence that people subconsciously process information about the planet’s magnetism.
-
 Health & Medicine
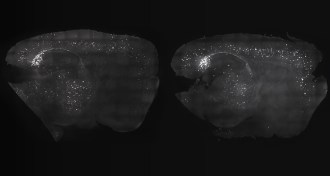
Health & MedicineFlickers and buzzes sweep mouse brains of Alzheimer’s plaques
Precisely timed clicking noises can counter signs of Alzheimer’s in the brains of mice and improve memory.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFDA has approved the first ketamine-based antidepressant
A nasal spray with a ketamine-based drug promises faster relief from depression for some people.
-
 Health & Medicine
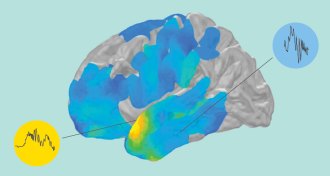
Health & MedicineRipples race in the brain as memories are recalled
A fast brain wave called a ripple often came before a person’s correct answer on a memory test.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow singing mice belt out duets
A precise timing system in the brain helps musical rodents from the cloud forests of Costa Rica sing to one another.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWatching hours of TV is tied to verbal memory decline in older people
The more television people age 50 and up watched, the worse they recalled a list of words in tests years later, a study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith its burning grip, shingles can do lasting damage
Varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles, may instigate several other problems.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain cells combine place and taste to make food maps
A select group of brain cells responds to both flavor and location, a specialty that may help an animal find the next good meal.