Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves common during sleep also show up in awake sheep
Sleep spindles, thought to help solidify memories in people, may do similar work during wakefulness if these daytime ripples occur in humans.
-
 Neuroscience
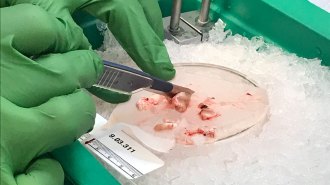
NeuroscienceLiving brain tissue experiments raise new kinds of ethical questions
An ethicist describes the quandaries raised by working with tissue involved in human awareness.
-
 Neuroscience
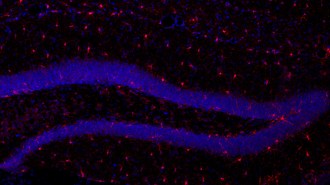
NeuroscienceBrain cells called microglia eat away mice’s memories
Immune cells that eliminate connections between nerve cells may be one way that the brain forgets.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceInjecting nanoparticles in the blood curbed brain swelling in mice
Nanoparticles divert inflammation-causing cells away from the brain after a head injury, a mouse study shows.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePsilocybin may help cancer patients with depression and anxiety for years
A study hints that a hallucinogen found in magic mushrooms could reshape how people cope with hard diagnoses over the long term.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow one woman became the exception to her family’s Alzheimer’s history
A single mutation in a woman who evaded Alzheimer’s may point to new ways to treat the disease.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA parasite that makes mice unafraid of cats may quash other fears too
The parasite Toxoplasma gondii can mess with all sorts of mice behaviors and make the rodents fearless in many situations.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice watching film noir show the surprising complexity of vision cells
Only about 10 percent of mice’s vision cells behaved as researchers expected they would, a study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
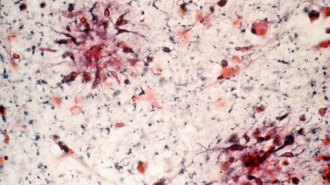
Health & MedicineA once-scrapped Alzheimer’s drug may work after all, new analyses suggest
An antibody that targets Alzheimer’s sticky protein amyloid showed promise in slowing mental decline, according to the company that’s developing it.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIs taking birth control as a teen linked to depression? It’s complicated
As researchers sift through conflicting data, no clear answers emerge on whether birth control during teenage years can cause depression later.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA dose of ketamine could lessen the lure of alcohol
Ketamine may weaken wobbly memories of drinking, a trick that might ultimately be useful for treating alcohol addiction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA protein helps disease-causing immune cells invade MS patients’ brains
Blocking the protein may hinder B cells invading the brain in multiple sclerosis, a study in mice and ‘stand-in’ human brain barriers finds.
By Sofie Bates