Neuroscience
-
 Animals
AnimalsA gene defect may make rabbits do handstands instead of hop
Mutations in a gene typically found throughout the nervous system rob rabbits of their ability to hop. Instead, the animals walk on their front paws.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, researchers treated chronic pain with electricity
In 1971, doctors eased chronic pain by sending electrical impulses to the spinal cord. Fifty years later, improved techniques help paralyzed people walk.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCatnip repels insects. Scientists may have finally found out how
The plant deters mosquitoes and fruit flies by triggering a chemical receptor that, in other animals, senses pain and itch.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThree visions of the future, inspired by neuroscience’s past and present
Three fantastical tales of where neuroscience might take us are based on the progress made by brain researchers in the last 100 years.
-
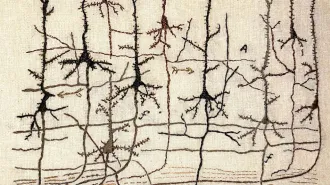 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFamous brain sketches come to life again as embroideries
A needlework project pays tribute to the iconic drawings of Spanish neuroscientist Santiago Ramón y Cajal.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice may ‘catch’ each other’s pain — and pain relief
Healthy mice mirror a companion’s pain or morphine-induced relief. Disrupting certain connections in the brain turns off such empathetic behaviors.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLonely brains crave people like hungry brains crave food
After hours of isolation, dopamine-producing cells in the brain fire up in response to pictures of humans, showing our social side runs deep.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePsilocybin may help treat depression, a small study finds
Researchers found that a compound in psychedelic mushrooms eased depression symptoms, but larger studies are needed.
-
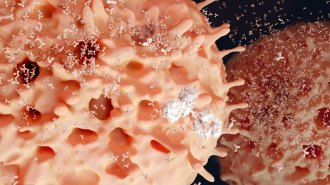 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineProtecting the brain from infection may start with a gut reaction
In mice, immune cells in the meninges are trained to battle infections in the gut before migrating to the brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFDA advisory panel declines to support a controversial Alzheimer’s treatment
The fate of an Alzheimer’s drug, developed by pharmaceutical company Biogen, remains up in the air.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA fish’s fins may be as sensitive to touch as fingertips
Newfound parallels between fins and fingers suggest that touch-sensing limbs evolved early, setting the stage for a shared way to sense surroundings.
-
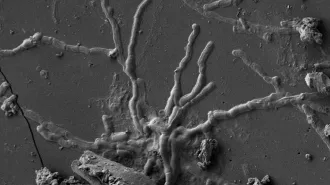 Anthropology
AnthropologyThese human nerve cell tendrils turned to glass nearly 2,000 years ago
Part of a young man’s brain was preserved in A.D. 79 by hot ash from Mount Vesuvius’ eruption.