Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
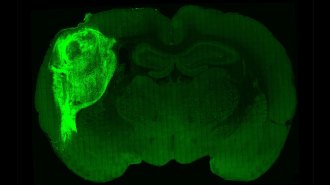
NeuroscienceClumps of human nerve cells thrived in rat brains
New results suggest that environment matters for the development of brain organoids, 3-D nerve cell clusters that grow and mimic the human brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhy traumatic brain injuries raise the risk of a second, worse hit
Recent hits to Miami Dolphins quarterback Tua Tagovailoa have reignited discussions of brain safety for professional football players. Brain experts weigh in.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Wonderful nets’ of blood vessels protect dolphin and whale brains during dives
Complex networks of blood vessels called retia mirabilia that are associated with cetaceans’ brains and spines have long been a mystery.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEmily Jacobs wants to know how sex hormones sculpt the brain
Emily Jacobs studies how the brain changes throughout women’s reproductive years, plus what it all means for health.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAn AI can decode speech from brain activity with surprising accuracy
Developed by Facebook’s parent company, Meta, the AI could eventually be used to help people who can’t communicate through speech, typing or gestures.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCOVID-19 gave new urgency to the science of restoring smell
With newfound pressure from the pandemic, olfactory training and a host of other newer treatments are now getting a lot more attention.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep deprivation may make people less generous
Helping each other is inherently human. Yet new research shows that sleep deprivation may dampen people’s desire to donate money.
By Sujata Gupta -
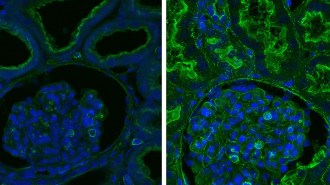 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAn hour after pigs’ deaths, an artificial system restored cellular life
Sensors, pumps and artificial fluid staved off tissue damage in pigs after cardiac arrest. The system may one day preserve organs for transplantation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSpinal stimulation gives some people with paralysis more freedom
Methods that stimulate the spine with electrodes promise to improve the lives of people with spinal cord injuries, in ways that go well beyond walking.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHerminia Pasantes discovered how taurine helps brain cells regulate their size
Mexican scientist Herminia Pasantes spent decades studying how nerve cells regulate their size and why it’s so vital.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow scientists are shifting their search for links between diet and dementia
Studies of food’s impact on Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are hampered by complexity. Scientists hope new research approaches prove more fruitful.
-
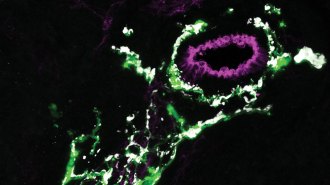 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGlial cells may take on big jobs in unexpected parts of the body
Scientists are finding mysterious glia in the heart, spleen and lungs and wonder what they’re doing there.