Microbes
-
 Life
LifeYoung squash bugs seek out adults’ poop for an essential microbe
Squash bug nymphs don’t rely on their parents to pick up a bacterium they’d die without. They find it on their own.
-
 Life
Life‘Polyester bees’ brew beer-scented baby food in plastic cribs
Ptiloglossa bees’ baby food gets its boozy fragrance from fermentation by mysteriously selected microbes.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeCoral reefs host millions of bacteria, revealing Earth’s hidden biodiversity
A new estimate of microbial life living in Pacific reefs is similar to global counts, suggesting many more microbes call Earth home than thought.
-
 Plants
PlantsA hunt for fungi might bring this orchid back from the brink
Identifying the fungi that feeds the Cooper’s black orchid in the lab may allow researchers to bank seeds and possibly regrow the species in the wild.
-
 Plants
PlantsSoil microbes that survived tough climates can help young trees do the same
Trees grown in soil with microbes that have survived drought and high or low temperatures have a better shot at survival when facing the same conditions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA has approved the first-ever vaccine for RSV
GSK’s shot, for those 60 and over, can protect against severe respiratory syncytial virus. Other vaccines, including to protect newborns, are in the works.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about upcoming vaccines and antibodies against RSV
New vaccines and monoclonal antibodies may be available this year to fend off severe disease caused by respiratory syncytial virus.
-
 Animals
AnimalsUrchins are dying off across the Caribbean. Scientists now know why
A type of single-celled microorganism associated with coral diseases is behind a sea urchin die-off in the Caribbean.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. cases of a deadly fungus nearly doubled in recent years
Though numbers are still small, clinical cases of Candida auris in the jumped 95 percent from 2020 to 2021, a CDC survey finds.
-
 Life
LifeChemical signals from fungi tell bark beetles which trees to infest
As fungi break down defensive chemicals in trees, some byproducts act as signals to bark beetle pests, telling them which trees are most vulnerable.
By Freda Kreier -
 Life
LifeFungi don’t turn humans into zombies. But The Last of Us gets some science right
Fungi like those in the post-apocalyptic TV show are real. But humans’ body temperature and brain chemistry may protect us from zombifying fungi.
-
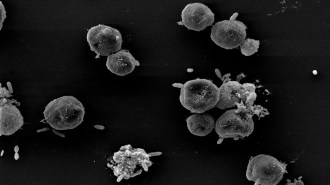 Microbes
MicrobesSome ‘friendly’ bacteria backstab their algal pals. Now we know why
The friendly relationship between Emiliana huxleyi and Roseobacter turns deadly when the bacteria get a whiff of the algae’s aging-related chemicals.
By Elise Cutts