Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow one scientist aims to boost Black people’s representation in genetic datasets
Through information sharing, geneticist Tshaka Cunningham wants to build trust and encourage more Black people to engage with the medical community.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal that pterosaurs puked pellets
Fish scale–filled pellets found by two pterosaurs are the first fossil evidence the flying reptiles regurgitated undigestible food, like some modern birds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDeep-sea Arctic sponges feed on fossilized organisms to survive
Slow-moving sponges, living deep in the Arctic Ocean where no currents deliver food, scavenge a carpet of long-dead critters.
-
 Plants
PlantsEarth may have 9,200 more tree species than previously thought
Estimating how many tree species are on Earth is an important step for forest conservation and protecting biodiversity.
By Jude Coleman -
 Animals
AnimalsMale elephant seals aim to get huge or die trying
Males will risk death to eat and grow as large as possible, since only the biggest males mate. But females aim for long-term survival.
By Jake Buehler -
 Archaeology
Archaeology‘Origin’ explores the controversial science of the first Americans
A new book looks at how genetics has affected the study of humans’ arrival in the Americas and sparked conflicts with Indigenous groups today.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsGory footage confirms orca pods can kill adult blue whales
For the first time, three recorded events show that orcas do hunt and eat blue whales using coordinated attacks that have worked on other large whales.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Animals
AnimalsVinegar eels can synchronize swim
Swarming, swimming nematodes can move together like fish and also synchronize their wiggling — an ability rare in the animal kingdom.
By Nikk Ogasa -
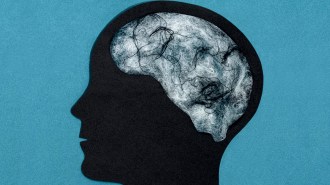 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA faulty immune response may be behind lingering brain trouble after COVID-19
The immune system’s response to even mild cases of COVID-19 can affect the brain, preliminary studies suggest.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA new device helps frogs regrow working legs after an amputation
A single treatment shortly after adult frogs lost part of their legs spurred regrowth of limbs useful for swimming, standing and kicking.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGut microbes help some squirrels stay strong during hibernation
Microbes living in the critters’ guts take nitrogen from urea and put it into the amino acid glutamine, helping squirrels retain muscle in the winter.
-
 Animals
AnimalsUrban animals may get some dangerous gut microbes from humans
Fecal samples from urban wildlife suggest human gut microbes might be spilling over to the animals. The microbes could jeopardize the animals’ health.