Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
- Animals
Deep Antarctic waters hold geometric communities of fish nests
Scientists found thousands of patterned fish nests in Antarctica’s Weddell Sea, boosting calls for marine protected areas.
By Carly Kay -
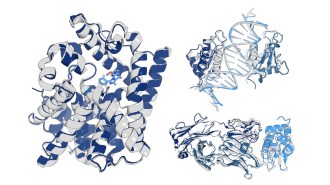 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceThe AI model OpenFold3 takes a crucial step in making protein predictions
The open-source AI model improves transparency in predicting how proteins interact with other molecules, which could speed up drug discovery.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPolar bears provide millions of kilograms of food for other Arctic species
A new study shows how much food polar bears leave behind — and how their decline threatens scavengers across the Arctic.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA reveals Neandertals traveled thousands of kilometers into Asia
DNA and stone tool comparisons suggest Eastern European Neandertals trekked 3,000 kilometers to Siberia, where they left a genetic and cultural mark.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsSubway mosquitoes evolved millennia ago in ancient Mediterranean cities
A variety of subway-dwelling mosquito seems like a modern artifact. But genomic analysis reveals the insect got its evolutionary start millennia ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaurs were thriving before the asteroid hit, new analysis suggests
New dating of New Mexico rocks suggest diverse dinosaurs thrived there just before the impact, countering the idea dinos were already on their way out.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhich venomous snakes strike the fastest?
Vipers have the fastest strikes, but snakes from other families can give some slower vipers stiff competition.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists and fishers have teamed up to find a way to save manta rays
Thousands of at-risk manta and devil rays become accidental bycatch in tuna fishing nets every year. A simple sorting grid could help save them.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMost women get uterine fibroids. This researcher wants to know why
Biomedical engineer Erika Moore investigates diseases that disproportionately affect women of color.
-
 Humans
HumansAn ancient bone recasts how Indigenous Australians treated megafauna
A new look at cuts on a giant kangaroo bone reveal First Peoples as fossil collectors, not hunters who helped drive species extinct, some scientists argue.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGuppies fall for a classic optical illusion. Doves, usually, do too
Comparing animals’ susceptibility to optical illusions can show how perception evolved.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Life
LifeA rice weevil frozen in flight won the 2025 Nikon Small World photo contest
From fluorescent ferns to sprawling neurons, this year’s winning photos reveal the structures and artistry of life seen through a microscope.
By Carly Kay