Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeSea sponges launch slow-motion snot rockets to clean their pores
Sea sponges rely on a sneezing mechanism to clear their pores, using mucus to flush out debris. This mucus provides food for other marine life.
By Jude Coleman -
 Animals
AnimalsRelocated beavers helped mitigate some effects of climate change
Along a river in Washington state, the repositioned beavers built dams that lowered stream temperatures and boosted water storage.
-
 Tech
TechScientists turned dead spiders into robots
In a new field dubbed “necrobotics,” researchers used a syringe and some superglue to control the dead bodies of wolf spiders.
By Asa Stahl -
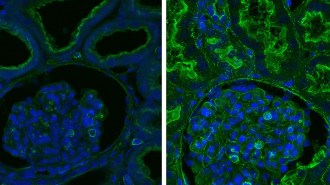 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAn hour after pigs’ deaths, an artificial system restored cellular life
Sensors, pumps and artificial fluid staved off tissue damage in pigs after cardiac arrest. The system may one day preserve organs for transplantation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSpinal stimulation gives some people with paralysis more freedom
Methods that stimulate the spine with electrodes promise to improve the lives of people with spinal cord injuries, in ways that go well beyond walking.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow slow and steady lionfish win the race against fast prey
Lionfish overcome speedy prey with persistent pursuit, waiting for the perfect moment to strike. Other slow predatory fish may use the technique too.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsWhale sharks may be the world’s largest omnivores
An analysis of the sharks’ skin shows that the animals eat and digest algae.
By Freda Kreier -
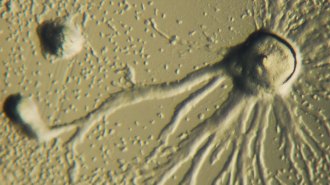 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny amoebas move faster when carrying cargo than without
A new study of the carrying capacity of single-celled amoebas may help scientists develop mini “trucks” to precisely target disease in the human body.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentElectrical bacteria may help clean oil spills and curb methane emissions
Cable bacteria are living electrical wires that may become a tool to reduce methane emissions and clean oil spills.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Life
LifeLike bees of the sea, crustaceans ‘pollinate’ seaweed
Crustaceans shuttle around red algae’s sex cells, helping the seaweed reproduce in a manner remarkably similar to flower pollination.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
Animals‘Murder hornets’ have a new common name: Northern giant hornet
Anti-Asian hate crimes helped push U.S. entomologists to give a colorful insect initially dubbed the Asian giant hornet a less inflammatory name.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFamine and disease may have driven ancient Europeans’ lactose tolerance
Dealing with food shortages and infections over thousands of years, not widespread milk consumption, may be how an ability to digest dairy evolved.
By Bruce Bower