Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
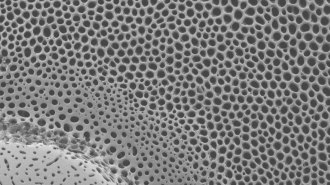
AnimalsSea urchin skeletons’ splendid patterns may strengthen their structure
“Voronoi” geometric patterns found in sea urchin skeletons yield strong yet lightweight structures that could inspire the creation of new materials.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExtreme climate shifts long ago may have helped drive reptile evolution
The end-Permian extinction left reptiles plenty of open ecological niches. But rapid climate change may be what kick-started the animals’ dominance.
By Beth Geiger -
 Life
LifeAn award-winning photo captures a ‘zombie’ fungus erupting from a fly
The winner of the 2022 BMC Ecology and Evolution photo competition captures a macabre cycle of life and death in the Peruvian Amazon.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy mosquitoes are especially good at smelling you
How Aedes aegypti mosquitoes smell things is different from how most animals do, making hiding human odors from the insects more complicated.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first known monkeypox infection in a pet dog hints at spillover risk
A person passed monkeypox to a dog. Other animals might be next, allowing the virus to set up shop outside of Africa for the first time.
-
 Humans
HumansWhy humans have more voice control than any other primates
Unlike all other studied primates, humans lack vocal membranes. That lets humans produce the sounds that language is built on, a new study suggests.
By Asa Stahl -
 Animals
AnimalsZoo gorillas use a weird new call that sounds like a sneezy cough
A novel vocalization made by the captive great apes may help them draw human attention.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeSea sponges launch slow-motion snot rockets to clean their pores
Sea sponges rely on a sneezing mechanism to clear their pores, using mucus to flush out debris. This mucus provides food for other marine life.
By Jude Coleman -
 Animals
AnimalsRelocated beavers helped mitigate some effects of climate change
Along a river in Washington state, the repositioned beavers built dams that lowered stream temperatures and boosted water storage.
-
 Tech
TechScientists turned dead spiders into robots
In a new field dubbed “necrobotics,” researchers used a syringe and some superglue to control the dead bodies of wolf spiders.
By Asa Stahl -
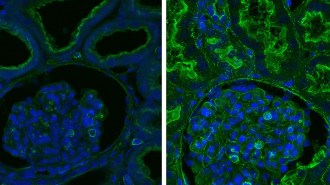 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAn hour after pigs’ deaths, an artificial system restored cellular life
Sensors, pumps and artificial fluid staved off tissue damage in pigs after cardiac arrest. The system may one day preserve organs for transplantation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSpinal stimulation gives some people with paralysis more freedom
Methods that stimulate the spine with electrodes promise to improve the lives of people with spinal cord injuries, in ways that go well beyond walking.