Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeAncient giant eruptions may have seeded nitrogen needed for life
A new study bolsters the idea that on the young Earth volcanic lightning may have provided some materials that made it possible for life to emerge.
By Bas den Hond -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnancy may hamper bats’ ability to ‘see’ in the dark
Tiny Kuhl’s pipistrelle bats make fewer calls when pregnant, which may make it more difficult to hunt prey, lab tests hint.
By Freda Kreier -
 Life
LifeSwarming locusts can deploy a chemical to avoid being cannibalized
Releasing a “don’t-eat-me” pheromone signals a locust has become a toxic treat. The finding could lead to new ways to control destructive swarms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA has approved the first-ever vaccine for RSV
GSK’s shot, for those 60 and over, can protect against severe respiratory syncytial virus. Other vaccines, including to protect newborns, are in the works.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA 2,200-year-old poop time capsule reveals secrets of the Andean condor
Guano that has accumulated in a cliffside Andean condor nest for 2,200 years reveals how the now-vulnerable birds responded to a changing environment.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThis marine biologist is on a mission to save endangered rays
Jessica Pate and the Florida Manta Project confirm that endangered mantas are mating and sicklefin devils are migrating along the East Coast.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists decoded people’s thoughts using brain scans
The finding may lead to better communication aids for people who can’t communicate easily. It also raises privacy concerns.
-
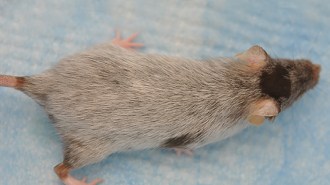 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouse hair turns gray when certain stem cells get stuck
Stem cells involved in giving hair its color must keep moving and changing maturity levels to prevent graying, a mouse study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHere are 5 cool findings from a massive project on 240 mammal genomes
A new series of studies on mammal genetics is helping scientists start to answer questions about evolution, cancer and even what makes us human.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about upcoming vaccines and antibodies against RSV
New vaccines and monoclonal antibodies may be available this year to fend off severe disease caused by respiratory syncytial virus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePets and people bonded during the pandemic. But owners were still stressed and lonely
People grew closer to their pets during the first two years of COVID. But pet ownership didn’t reduce stress or loneliness, survey data show.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhat was Rosalind Franklin’s true role in the discovery of DNA’s double helix?
Two researchers say that Rosalind Franklin knowingly collaborated with James Watson and Francis Crick to discover the molecular structure of DNA.