Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeMany frogs glow in blue light, and it may be a secret, eerie language
Biofluorescence is far more common across frog species than previously thought. The faint twilight glow could have a role in communication or mating.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMeet the tiny ancient whale named after King Tut
The newly discovered Tutcetus rayanensis lived about 40 million years ago. It was just 2.5 meters long and weighed less than 200 kilograms.
By Skyler Ware -
 Plants
PlantsThe fastest-evolving moss in the world may not adapt to climate change
The genus Takakia has the largest number of fast-evolving genes of any moss, a study finds. But it’s losing ground in the warming Himalayas.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe ‘unknome’ catalogs nearly 2 million proteins. Many are mysterious
Scientists have unveiled a new database that emphasizes how much we still don’t know about human proteins and genes.
By Skyler Ware -
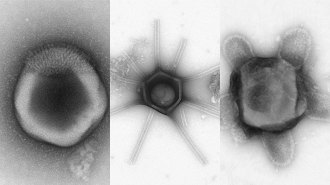 Life
LifeA fantastical world of potential giant viruses lurks beneath the soil
Giant viruses were already known for their large sizes. A close look at a scoop of soil shows that they may come in a variety of funky shapes as well.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA colossal ancient whale could be the heaviest animal ever known
Perucetus colossus may have tipped the scales at up to 340 metric tons, but some scientists are skeptical it could have sustained that mass.
By Skyler Ware -
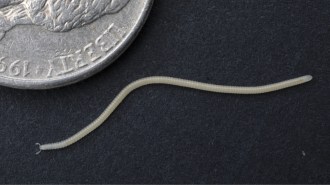 Animals
AnimalsThe newfound Los Angeles thread millipede is ready for its close-up
Found in Southern California, Illacme socal is the third of its genus found in North America, with the rest of its relatives scattered around the world.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePlayful behavior in rats is controlled by a specific area of their brains
Cells in a brain region called the periaqueductal gray are activated by chasing and tickling, a study finds. Blocking their activity reduces play in rats.
By Simon Makin -
 Math
MathHow geometry solves architectural problems for bees and wasps
Adding five - and seven - sided cells in pairs during nest building helps the colonyfit together differently sized hexa gonal cells , a new study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome African birds follow nomadic ants to their next meal
Specialized interactions between birds and driver ants in Africa could help explain why the birds are especially sensitive to forest disturbances.
By Yao-Hua Law -
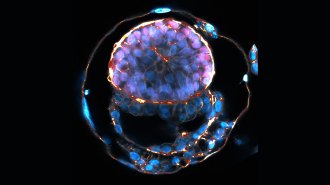 Humans
HumansHuman embryo replicas have gotten more complex. Here’s what you need to know
Lab-engineered human embryo models created from stem cells provide a look at development beyond the first week. But they raise ethical questions.
-
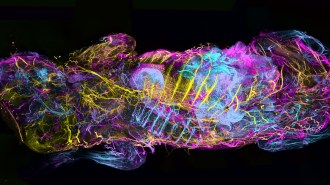 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith a new body mapping technique, mouse innards glow with exquisite detail
Removing cholesterol from mouse bodies lets fluorescently labeled proteins infiltrate every tissue, helping researchers to map entire body systems.