Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe right bacterial mix could help frogs take the heat
Wood frog tadpoles that receive a transplant of green frog bacteria can swim in warm waters, revealing another role for microbiomes: heat tolerance.
-
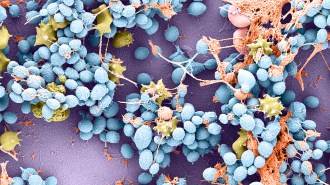 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow a deadly fungus is so good at sticking to skin and other surfaces
One of Candida auris’ scary superpowers is its stick-to-itiveness. Unlike other fungi, the pathogen uses electrical charges to glom onto things.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew computer analysis hints volcanism killed the dinosaurs, not an asteroid
Scientists take a creative approach to investigating what caused the mass extinction 66 million years ago, but the debate is far from settled.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA one-of-a-kind trilobite fossil hints at what and how these creatures ate
The preserved contents suggest the trilobite fed almost continuously and had a gut environment with an alkaline or neutral pH, researchers say.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsSeen Bigfoot or the Loch Ness Monster? Data suggest the odds are low
Floe Foxon is a data scientist by day. But in his free time, he applies his skills to astronomy, cryptology and sightings of mythical creatures.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsThese brainless jellyfish use their eyes and bundles of nerves to learn
No brain? No problem for Caribbean box jellyfish. Their seemingly simple nervous systems can learn to avoid obstacles on sight, a study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow brain implants are treating depression
This six-part series follows people whose lives have been changed by an experimental treatment called deep brain stimulation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceToday’s depression treatments don’t help everyone
In the second story in the series, deep brain stimulation is a last resort for some people with depression.
-
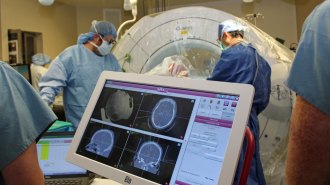 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe science behind deep brain stimulation for depression
The third part of the series explores the promising brain areas to target for deep brain stimulation for depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat’s it like to live with deep brain stimulation for depression?
The fourth article in the series explores the physical and emotional challenges of experimental brain implants for depression.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThere’s a stigma around brain implants and other depression treatments
The fifth article in the series asks why people are so uncomfortable with changing the brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat’s the future of deep brain stimulation for depression?
The final story of the series describes efforts to simplify and improve brain implants for severe depression.