Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dinosaur species is titanic
Titanoceratops may be the oldest known member of the triceratops group.
By Susan Milius -
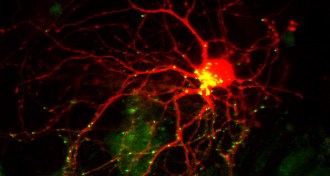
 Life
LifeGenes & Cells
A new type of intestinal cell is discovered, plus nuclear fallout and a new Parkinson's culprit in this week's news.
By Science News -
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLight-sensor pulls perplexing double duty
A long-studied eye pigment appears to also detect temperature, a study in fruit flies shows.
-
 Life
LifeLife
Chimps are righties and orangutans lefties, plus singing mice and chilly dinosaurs in this week's news.
By Science News -
 Humans
HumansMissing bits of DNA may define humans
Genetic information lost along the way may have led to bigger brains and spineless penises, among other traits.
-
 Life
LifeAnxiety switch makes mice shy no more
Brain-control experiments could help shed light on psychiatric disorders
-
 Life
LifeHelp, elephants need somebody
In pull-together tests, pachyderms are on par with chimps in understanding the basics of cooperation.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeGood gene type for cancer bad for stroke
A DNA variant that helps prevent tumors may diminish the brain’s recovery after an interruption in blood supply.
-
 Life
LifeLife
Bats are savvy shoppers for insect snacks, plus heartless dinos and worm evolution in this week’s news.
By Science News -
 Life
LifeHagfish may eat through their skin
The odd dining habits of carrion-eating protovertebrates may be relevant to the evolutionary transition to land.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeLab-engineered organism fights malaria
A new breed of poison-secreting fungi can kill parasites in a mosquito.