Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA decades-old mystery has been solved with the help of newfound bee species
Masked bees in Australia and French Polynesia have long-lost relatives in Fiji, suggesting that the bees’ ancestors island hopped.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBig monarch caterpillars don’t avoid toxic milkweed goo. They binge on it
Instead of nipping milkweed to drain the plants’ defensive sap, older monarch caterpillars may seek the toxic sap. Lab larvae guzzled it from a pipette.
By Susan Milius -
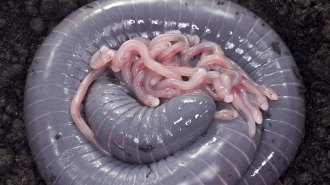 Life
LifeThis is the first egg-laying amphibian found to feed its babies ‘milk’
Similar to mammals, these ringed caecilians make a nutrient-rich milk-like fluid to feed their mewling hatchlings up to six times a day.
By Jake Buehler -
 Environment
EnvironmentHow air pollution may make it harder for pollinators to find flowers
Certain air pollutants that build up at night can break down the same fragrance molecules that attract pollinators like hawk moths to primroses.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSee 3-D models of animal anatomy from openVertebrate’s public collection
Over six years, researchers took CT scans of over 13,000 vertebrates to make museum collections more easily accessible to researchers and the public.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe desert planet in ‘Dune’ is plausible, according to science
Humans could live on the fictional planet Arrakis from Dune but (thankfully) no giant sandworms would menace them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant tortoise migration in the Galápagos may be stymied by invasive trees
An invasion of Spanish cedar trees on Santa Cruz Island may block the seasonal migration routes of the island's giant tortoise population.
By Jake Buehler -
 Genetics
GeneticsA genetic parasite may explain why humans and other apes lack tails
Around 25 million years ago, a stretch of DNA inserted itself into an ancestral ape’s genome, an event that might have taken our tails away.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe Brazilian flea toad may be the world’s smallest vertebrate
Brazilian flea toads are neither a flea nor a toad, but they are almost flea-sized. The frogs are small enough to fit on a pinkie fingernail.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSnake venom toxins can be neutralized by a new synthetic antibody
A lab-made protein protected mice from lethal doses of paralyzing toxins found in a variety of snakes, a new study reports.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Plants
PlantsOn hot summer days, this thistle is somehow cool to the touch
In hot Spanish summers, the thistle Carlina corymbosa is somehow able to cool itself substantially below air temperature.
-
 Plants
PlantsAncient trees’ gnarled, twisted shapes provide irreplaceable habitats
Traits that help trees live for hundreds of years also foster forest life, one reason why old growth forest conservation is crucial.
By Jake Buehler