Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe secret behind the alligator’s toothy smile
Dental stem cells enable the reptile to grow new teeth every year, researchers find.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsCannibalistic spiders may just be choosy guys
Male Micaria sociabilis may choose to have older female for lunch, not sex.
By Susan Milius -
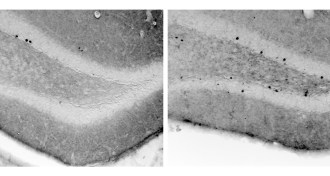 Life
LifeExploration forges differences in identical twins
Mice with the same genes and surroundings diverged in brain development depending on how much they moved around their environment.
-
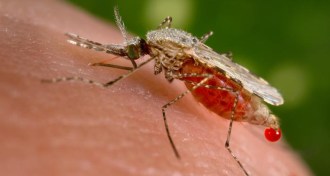 Animals
AnimalsMalaria mosquito dosed with disease-fighting bacteria
After thousands of tries, lab gets parasite-carrying insect to catch Wolbachia.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeGut bacteria adapt to life in bladder
E. coli moving between systems may cause urinary tract infections.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Humans
HumansEurope is one big family
Continent's ancestry merges about 30 generations ago, genetic study finds
By Meghan Rosen -

-
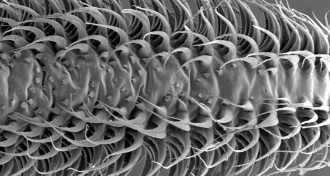 Animals
AnimalsTongue bristles help bats lap up nectar
High-speed videos capture stretched-out tongue bumps that stretch out so nectar-feeding bats can slurp up their food.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePieces of Light
How the New Science of Memory Illuminates the Stories We Tell About Our Pasts by Charles Fernyhough.
By Science News -
 Animals
AnimalsWinged robots may shed light on fly aerobatics
After years of trying, researchers create flapping machines that can hover and perform rudimentary flight maneuvers.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEvolutionary enigmas
Comb jelly genetics suggest a radical redrawing of the tree of life.
By Amy Maxmen -
 Animals
AnimalsDeep-sea worms drop acid to get dinner
Bone-eating worms produce chemicals to dissolve and feed on skeletons.