Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEye-tracking cameras show peahens’ wandering gaze
Data show that female birds are not so riveted by their suitors’ magnificence
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeRogue genes on X chromosome turn on in testicles
Chunks of rapidly evolving DNA could affect sperm production in males.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins name themselves with a whistle
The marine mammals respond only to their own handles.
By Meghan Rosen -
-
 Life
LifeGut microbes get first dibs on heart meds
Some people harbor a strain of bacteria that chews through cardiac medication before it can treat symptoms.
-
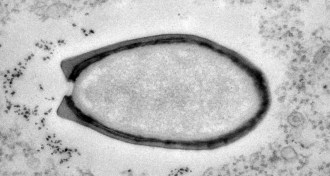 Life
LifeSize isn’t only mystery of huge virus
A strange replication method and an unusual genetic sequence are among the mysteries of the outsized Pandoravirus.
-
 Life
LifeMicrobes can draw the line between species
Wasps' gut inhabitants can kill or save crossbreeds.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeStem cells made with just seven chemicals
Chemical cocktail turns adult mouse cells into embryonic-like ones.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsTechnique inactivates Down-causing chromosome
Though far from a cure, the advance could eventually lead to gene therapy that alleviates some symptoms.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFattened livers prep white sharks for extreme migrations
The organ's reserves enable a long journey from waters off California to Hawaii and back, tracking data suggest.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaur had impressive schnoz
Fossils found in Utah reveal geographic segregation of horned species.
By Erin Wayman -