Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeTigers meet, mix in forest corridors
In India, narrow strips of wild land connect small groups of cats.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOxygen boost aided carnivore evolution in Cambrian explosion
Atmospheric change and rise of predators caused burst in complexity of life.
By Erin Wayman -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrainwashed
The Seductive Appeal of Mindless Neuroscience by Sally Satel and Scott O. Lilienfeld.
By Bruce Bower -

-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe Anorexic Brain
Neuroimaging improves understanding of eating disorder.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeA flash of light implants false memories in mice
Researchers alter rodents' recollections by exciting just a few neurons.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEye-tracking cameras show peahens’ wandering gaze
Data show that female birds are not so riveted by their suitors’ magnificence
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeRogue genes on X chromosome turn on in testicles
Chunks of rapidly evolving DNA could affect sperm production in males.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins name themselves with a whistle
The marine mammals respond only to their own handles.
By Meghan Rosen -
-
 Life
LifeGut microbes get first dibs on heart meds
Some people harbor a strain of bacteria that chews through cardiac medication before it can treat symptoms.
-
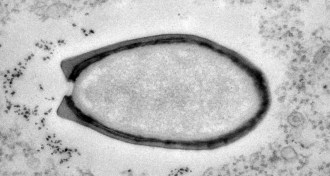 Life
LifeSize isn’t only mystery of huge virus
A strange replication method and an unusual genetic sequence are among the mysteries of the outsized Pandoravirus.