Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCollision Course
The tales of two ornithologists trying to prevent birds colliding with windows highlight the obstacles facing applied biology.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsRats induced into hibernation-like state
Injection of compound causes animals to slow heartbeat, lower body temperature.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceVideo game sharpens up elderly brains
Adults over 60 who played for several hours a month beat untrained 20-year-olds in racing game.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew fungus species found killing salamanders
First there was amphibian killer fungus Bd. Now there's Bs.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsTraveling with elders helps whooping cranes fly straight
Rare data show birds get more efficient the more they migrate along route between Wisconsin and Florida.
By Susan Milius -
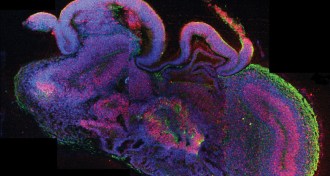 Life
LifeTiny human almost-brains made in lab
Stem cells arrange themselves into a version of the most complex human organ.
-
 Life
LifeFlu antibodies can make disease worse
Pigs vaccinated against one influenza virus got lung damage if infected with another strain.
-
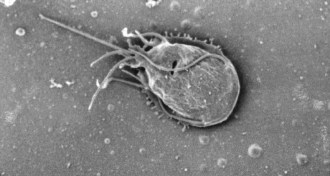 Life
LifeA fight between gut parasites means a win for people
Worms and Giardia can antagonize each other in the human intestinal tract, study of people in the Amazon suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPorpoises Can Teach Man Marine Diving, Detection
Excerpt from the September 7, 1963, issue of Science News Letter
By Science News -
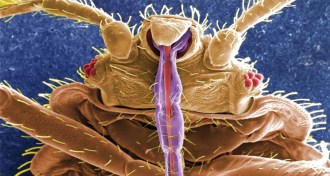 Microbes
MicrobesLet the bedbugs bite
Harold Harlan has been feeding bedbugs, intentionally, on his own blood since 1973. He keeps pint or quart jars in his home containing at least 4,000 bugs.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeBats can carry MERS
DNA of a deadly respiratory virus has been found in a Saudi Arabian mammal.
-
 Life
LifeNatural antifreeze prevents frogsicles
Sugar and other chemicals keep Alaskan frogs from freezing completely.
By Meghan Rosen