Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Humans
HumansBrain research goals laid out
NIH details priority areas, including improving imaging technology and mapping brain structures.
-
 Neuroscience
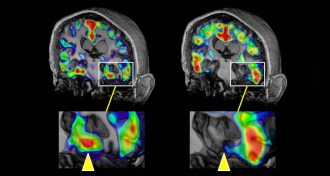
NeuroscienceA beacon illuminates a key Alzheimer’s protein
In PET scans, researchers can now see tau, which accompanies amyloid in diseased brains.
-
 Humans
HumansChemical behind corked wine quashes other aromas
Old sock smell signals contamination but doesn't belong to TCA, study proposes.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes for body symmetry may also control handedness
Lefties and righties can thank same genes that put hearts on left side for hand dominance, study of thousands of people’s DNA suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYoung insect legs have real meshing gears
Tiny teeth on hiplike structures keep legs in sync, allowing juvenile planthoppers to jump.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsHumpbacks make a comeback in British Columbia
Whale numbers double at a feeding site in Canada.
-
 Microbes
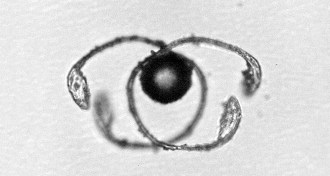
MicrobesHorsetail spores don’t need legs to jump
Forget legs. A plant uses curly, humidity-controlled ribbons to make epic leaps.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsAvoiding feces may be ‘luxury’ wild mice can’t afford
For a mouse in the woods, finding any food at all may trump poopy locations.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeMany genes in dolphins and bats evolved in the same way to allow echolocation
Widespread changes scattered across the genomes of distantly related species cooperated to craft the trait.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSeeking the loneliest whale
An enigmatic whale roams the North Pacific, and next year Bruce Mate will lead a monthlong expedition to find it.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsCollision Course
The tales of two ornithologists trying to prevent birds colliding with windows highlight the obstacles facing applied biology.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsRats induced into hibernation-like state
Injection of compound causes animals to slow heartbeat, lower body temperature.