Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-

-
 Animals
AnimalsHibernating turtles don’t slip into a coma
Winterized red-eared sliders shut down their lungs but spring into action when they see light.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Decoding Annie Parker’ portrays hunt for breast cancer genes
Not long ago, most doctors scoffed at the idea of a “cancer gene,” as the new film shows.
-
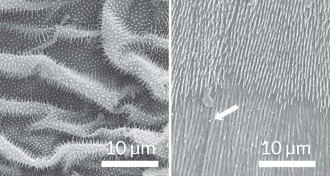 Animals
AnimalsLegless geckos slither using skin ridges
The animal's belly has flat rows of ripples that may help them wriggle.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsAlpine swifts fly nonstop for more than six months
During a journey of 200 days, the birds eat, rest and migrate without touching the ground.
-

-
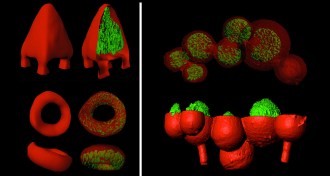 Life
Life3-D printing builds bacterial metropolises
By simulating biofilms, new 3-D printing technique may help researchers study antibiotic resistance.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrainy videos
A short film that uses humor and science to explain congenital anosmia has won the Society for Neuroscience’s 2013 Brain Awareness Video Contest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMedicine Nobel goes to cellular transport research
Honor given to three scientists who discovered how machinery moves cargo around cells.
By Science News -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCellular transport research wins Nobel Prize in medicine or physiology
Guest post by Tina Hesman Saey and Nathan Seppa.
By Science News -
 Animals
AnimalsHiding up your nose is a clever strategy for ticks
Found hiding in the noses of Ugandan chimps, a new tick species hitchhiked its way to America in a researcher's nose.
-
 Life
LifeBlocking a hormone helps mice beat lengthy jet lag
A timekeeping brain molecule steadies the beat of the circadian clock, while stopping it allows for a quick reset.