Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAutism may be detectable in baby’s first months of life
Infants later diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder lose tendency to gaze at others’ eyes during first half-year, researchers find.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBirds avoid the sounds of roads
The sound of cars driving down a road is enough to deter many bird species from an area.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Bearded ladies’ are less sexy to male lizards
Females with masculine neck marks are passed over as mates.
-
 Life
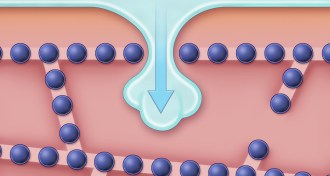
LifeIce crystals form along cells’ seamlike structures
A detailed view of how ice forms among cells could lead to better tissue preservation.
-
 Paleontology
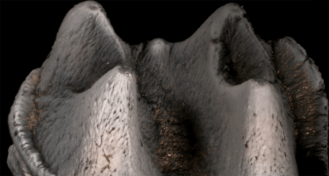
PaleontologyGiant platypus tooth found
A fossil molar found in Australia reveals a previously unknown extinct species of the mammal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe reefs are alive with the sound of oysters
How does an oyster figure out where to settle down in life? It listens for where the party’s at. A new study shows that oyster larvae can detect sound in the water.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphin without a name
While splitting the dolphin family tree, researchers found a new species.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain enables sight without light
Sensory cross talk may underlie ability to see one’s own hand moving when it’s pitch black.
By Bruce Bower -

-

-
 Animals
AnimalsWag the dog: When left vs. right matters
Most of us see a wagging dog’s tail and automatically think it’s a good sign. But are some wags more friendly than others? A new study says yes.
-
 Neuroscience
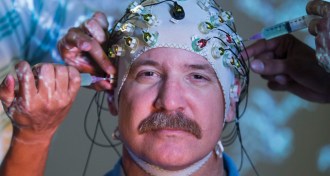
NeuroscienceMind to motion
Brain-computer interfaces promise new freedom for the paralyzed and immobile.
By Meghan Rosen