Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
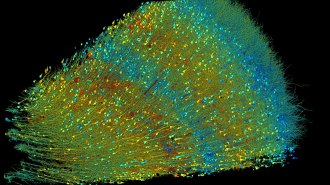
NeuroscienceBiological puzzles abound in an up-close look at a human brain
Mirror-image nerve cells, tight bonds between neuron pairs and surprising axon swirls abound in a bit of gray matter smaller than a grain of rice.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTwo distinct neural pathways may make opioids like fentanyl so addictive
A study in mice looked at how feelings of reward and withdrawal that opioids trigger play out in two separate circuits in the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman body lice could harbor the plague and spread it through biting
Rats and fleas previously got all the blame, but humans’ own parasites could be involved.
-
 Environment
Environment‘The High Seas’ tells of the many ways humans are laying claim to the ocean
The book explains how the race for ocean resources from fish to ores to new medicines — the Blue Acceleration — is playing out.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSumatran orangutans start crafting their engineering skills as infants
By 6 months old, young orangutans are experimenting with construction materials, and by 6 years old, they are building platforms 20 meters in the air.
-
 Neuroscience
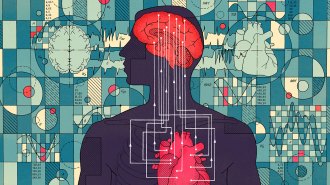
NeuroscienceThe heart plays a hidden role in our mental health
Deciphering the messages that the heart sends to the brain could lead to new anxiety treatments and even unlock the secrets of consciousness.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetic analyses of the bird flu virus unveil its evolution and potential
The H5N1 outbreak in cattle is giving flashbacks to the COVID pandemic. But this time is different.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow smart was T. rex?
A debate over how to count neurons in dinosaurs is raising questions about how to understand extinct animals’ behavior.
By Freda Kreier -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow did an ancient shark parasite end up fossilized in tree resin?
A worm preserved in 99-million-year-old amber resembles modern flatworms in shark intestines. The rare finding has scientists stumped.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiger beetles may weaponize ultrasound against bats
In response to recordings of echolocating bats, tiger beetles emit noises that mimic toxic moths that bats avoid.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCows might host both human and bird flus
Both kinds of influenza viruses may break into cattle cells using receptors similar to those in people, wild birds and poultry.
-
 Earth
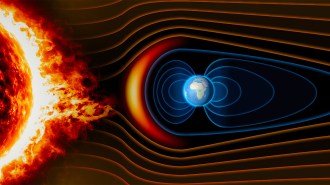
EarthA weaker magnetic field may have paved the way for marine life to go big
Decreased protection from cosmic radiation may have increased oxygen levels in the atmosphere and oceans, allowing animals to grow larger.