Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
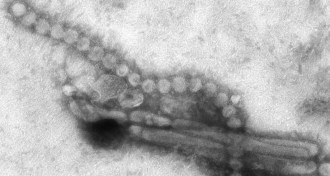
LifeH7N9 flu still better adapted to infect birds over humans
The proteins from the avian flu appear better suited for attaching to bird, not human, molecules.
-
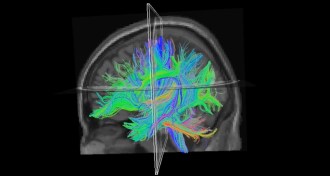 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFaulty brain wiring may contribute to dyslexia
Adults with the disorder showed difficulty transmitting information among areas that process language.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeAutism may have link to chemicals made by gut microbes
Beneficial bacteria improved abnormal behaviors in mice with altered intestines.
-
 Life
LifeTargeting single set of nerve cells may block mosquitoes
The insects use the same neurons to detect carbon dioxide from our breath and odors from our skin so blocking those cells could lead to more simplified repellent systems.
-
 Life
LifeMale contraceptive test targets sperm’s travel route
Most efforts at a male contraceptive have focused on hormones, trying to stop production of sperm. A new study in mice explores leaving the sperm to themselves, and instead stops their transport.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceExcess activity shrinks blood vessels in baby mouse brains
Newborn mouse pups experience permanent brain changes when repeatedly overstimulated.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow the ghost shark lost its stomach
The lack of a digestive organ in fish and other animals is linked to genetics.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsEvolution of venom, binge eating seen in snake DNA
Python and cobra genes evolved quickly to enable hunting strategies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow koalas sing low
Extra set of vocal cords lets males hit surprisingly low notes.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFear can be inherited
Parents’ and even grandparents’ experiences echo in offspring, a study of mice finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGlobal neuro lab
With more than 50 million users, the brain-training website Lumosity is giving scientists access to an enormous collection of cognitive performance data. Mining the dataset could be the first step toward a new kind of neuroscience.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDNA study reveals new wild cat species in Brazil
A new small cat species, Leopardus guttulus, was discovered in Brazil, hiding in plain sight. The oncilla, researchers say, is really two kinds of cat.