Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFootball helmet redesign can reduce concussion risk
No helmet will ever eliminate the risk of sustaining a concussions during a football game. But tweaking the design may slow the speed of head movements after a hit and reduce the risk of brain trauma.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDisco clams put on a streak show
Scuba divers call Ctenoides ales the disco or electric clam because the restless, curling lips of its mantle flash bright streaks.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsSynchronous birth
For young banded mongoose moms, there’s only one choice for when to give birth — the same day as older, dominant mothers. In communities of these cat-sized animals, all females give birth together, no matter when they became pregnant.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen snakes fly
A gliding snake gets some lift by spreading its ribs, but much about its flight remains a mystery.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTumors grow faster in cancer-prone mice given vitamins
The tumors killed the mice twice as fast as early-stage lung lesions in mice not given the antioxidants, researchers report.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmunotherapy attacks aberrant cervical growth
The treatment might stop cancers before they arise.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Plants
PlantsSexually deceived flies not hopelessly dumb
Pollinators tricked into mating with a plant become harder to fool a second time.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineH7N9 flu makes a comeback
Scientists warn that the risk that the illness could spread remains.
-
 Life
LifeA little acid or a tight squeeze can turn a cell stemlike
Stresses send mouse cells into primordial state capable of making any tissue.
-
 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Unique’ human brain regions similar to monkeys’ brains
Monkeys may have rudimentary brain wiring that later evolved into the connections that gave humans the ability to understand language, think flexibly and make decisions.
-
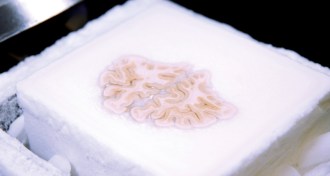 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFamous brain surgery patient H.M. retained a chunk of hippocampus
The patient's amnesia was probably due to the loss of other regions and neural connections.
-
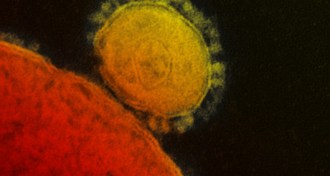 Life
LifeMolecule stops MERS spread among cultured human cells
The molecule interacts with the protein the MERS virus uses to enter a cell.