Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
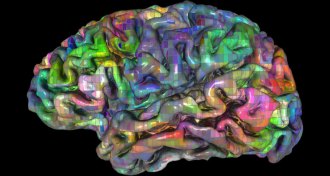 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWays of seeing the brain inspire notions of how it works
As scientists have developed more sophisticated methods and ideas, their understanding of how the brain works has shifted too.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOrangutans hit the ground walking
A surprising affinity for moving across the forest floor may aid threatened apes.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeHappy birthday, Mr. Darwin
A male rove beetle that Charles Darwin collected in Argentina in 1832 has finally turned up and been named in his honor.
-
 Life
LifeNonhuman city natives in decline but can be conserved
Cities have been a downer on biodiversity but native populations still remain in urban areas, offering a starting point for possible conservation efforts.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrug injection could limit heart attack damage
Study in pigs suggests hydrogel treatment might minimize the risk of heart failure in survivors.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Humans
HumansClovis baby’s genome unveils Native American ancestry
DNA from skeleton shows all tribes come from a single population.
-
 Life
LifeCharms of small males may collapse a Darwin’s finch species
Mating rules may be changing for one of the storied Galápagos birds.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFeedback
Calculating vaccines' impact, cat-induced bird death toll revised, taming wildcat genetics, and praise for The Science Life.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe Ice Age was harsh on orcas
Killer whale DNA shows that climate change resulted in declines for most populations.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsOrigin of Tibetans’ high-altitude adaptations found
Mixing genes of two ancestral populations gave modern Tibetans their ability to withstand high altitude.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBad kitty: Cat bites can cause nasty infections
Three in 10 patients seeking treatment for hand bites were hospitalized, study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
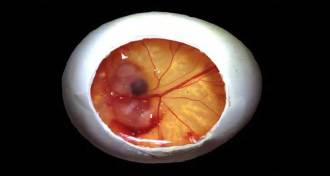 Animals
AnimalsEmbryos in eggs move to get comfy
Even before hatching, Chinese alligators, snapping turtles and some relatives can shift toward favorable temperatures.
By Susan Milius