Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMice lose a gene to drop some weight
Mice lacking gene have less fat, more muscle and lived longer than normal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMama frog’s care includes a gift of poison
Strawberry poison frog tadpoles get defensive chemicals through unfertilized, nutritious eggs provided by mom.
-
 Life
LifeTo do: Exhibits to explore in the U.S. and London
Highlights include the impending arrival of a T. rex skeleton in Washington, D.C., a pterosaur exhibit coming to New York City, and the history of longevity at the Royal Society in London.
-
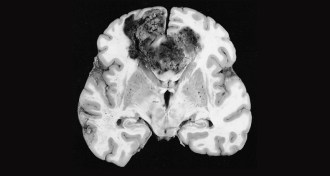 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSmall molecule makes brain cancer cells collapse and die
A small molecule, Vacquinol-1, may provide a different way to target and kill cells in glioblastomas, a type of brain tumor.
-
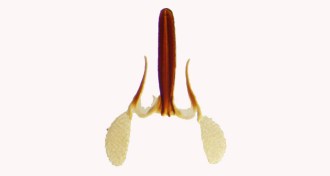 Plants
PlantsMilkweed ‘horns’ may equal wins in reproduction battle
Plants may be ripping a page right from bucks’ playbooks, developing hornlike weapons to improve their chances of reproduction.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA parasitic cuckoo can be a good thing
Great spotted cuckoo chicks show that brood parasites may benefit their hosts.
By Susan Milius -
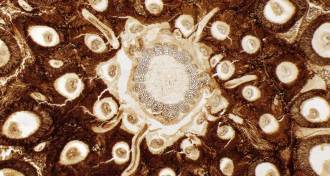 Plants
PlantsFossil fern showcases ancient chromosomes
Fossil nuclei and chromosomes seen in a 180-million-year-old fern reveals that the plants have stayed mostly the same.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeHuman noses know more than 1 trillion odors
Sense of smell displays a vast reach in study of people’s ability to distinguish between scents.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCalcium in alcoholism drug may be what prevents relapse
Acamprosate, one of the few drugs to treat alcoholism, may be nothing more than a vehicle for a calcium supplement.
-
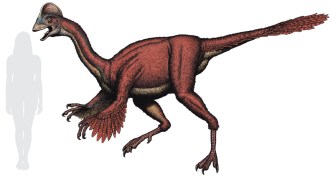 Paleontology
PaleontologyThe dinosaur ‘chicken from hell’
Fossils suggest that a supersized chickenlike reptile called Anzu wyliei roamed what are now the Dakotas roughly 67 million years ago.
-
 Life
LifeVitamin A deficit in the womb hurts immune development
Mice deprived of vitamin A in utero grow up with undersized immune organs.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsOwl monkeys’ fidelity linked to males’ quality of parenting
The evolution of animals’ sexual fidelity is probably linked to the intensity of male care, the researchers suggest.