Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly meat-eater may have led to larger plant-eaters
The newly identified Eocasea martini may have set the stage for later, much larger animals to become plant-eaters.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene activity sets humans apart from extinct hominids
Differences in gene activity caused by DNA methylation distinguish modern people from Neandertals and Denisovans.
-
 Animals
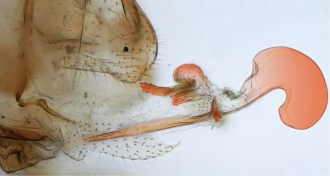
AnimalsMost extreme female penis is found on cave lice
Female penis, male vagina have been discovered in tiny Brazilian insects.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
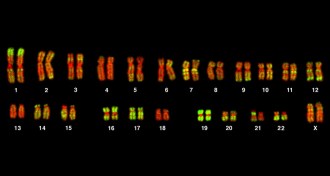
GeneticsDown’s syndrome goes beyond chromosome 21
A genetic analysis suggests that the DNA changes linked to Down's syndrome happen on all chromosomes, not just the 21st.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScent of a fruit fly larva comes from its gut microbes
Microbes in the guts of fly larvae produce smells that attract fruit flies.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesOne giant leap for zit-causing microbes
A bacterium that lives on humans and causes acne also hopped to domesticated grapevines and relies on the plant for crucial DNA repairs.
-
-
 Neuroscience
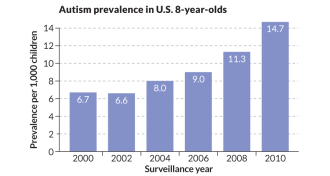
NeuroscienceWhat’s behind rising autism rates
Better diagnosis may be driving a recent spike in autism.
-
 Life
LifeFind your inner fish with PBS series on human evolution
A new documentary explores how the human body came together over 3.5 billion years of animal evolution.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTriclosan aids nasal invasions by staph
The antimicrobial compound triclosan, commonly found in soaps and toothpaste, may help Staphylococcus aureus stick around.
By Beth Mole -
 Genetics
GeneticsModern hunter-gatherers’ guts host distinct microbes
A healthy collection of gut bacteria depends on the environment in which people live and their lifestyle, research shows.
-
 Climate
ClimateReef fish act drunk in carbon dioxide–rich ocean waters
In first test in the wild, fish near reefs that bubble with CO2 lose fear of predators’ scent.
By Meghan Rosen