Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
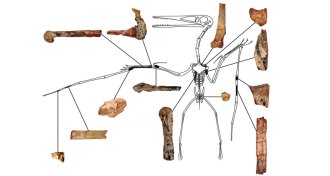
Paleontology‘Hidden dragon’ fossil is oldest flying reptile
Researchers have unearthed the oldest pterodactyl ever discovered: Kptodrakon progenitor soared over the Earth 163 million years ago.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsY chromosome gets a closer examination
The Y chromosome may play a larger role in Turner syndrome and in health and disease differences between males and females than previously thought.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA guide to the world’s biggest flightless birds
A rhea on the loose in England has prompted warnings about approaching the bird. From ostriches to cassowaries, here’s your guide to friendly and unfriendly big birds.
-
 Climate
ClimateGlacial microbes gobble methane
While some bacteria produce methane in Greenland’s melting ice sheet, others may consume the greenhouse gas as it escapes.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
AnimalsFrustrated fish get feisty
Smaller rainbow trout become more aggressive towards bigger fish when they don’t their usual treats.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsFarmers assimilated foragers as they spread agriculture
While some European hunter-gatherers remained separate, others mated with the early farmers that introduced agriculture to the continent.
-
 Genetics
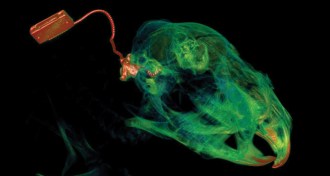
GeneticsGene therapy with electrical pulses spurs nerve growth
Deaf guinea pigs' hearing improves with electrical pulses from a hearing implant are combined with gene therapy, a new study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSecrets of a sailfish attack
The large, long-nosed sailfish use their rostrums more like a sword than a spear to attack prey.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins use sponges to dine on different grub
The animals can learn to use tools to exploit food sources that would be otherwise unavailable, a study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRainbow trout genome shows how genetic material evolved
The finding challenges the idea that whole genome duplications are followed by quick, massive reorganization and deletions of genetic material.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSubmariners’ ‘bio-duck’ is probably a whale
First acoustic tags on Antarctic minke whales suggest the marine mammals are the long-sought source of the mysterious bio-duck sound.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePain curbs sex drive in females, but not males
When in pain, female mice’s interest in sex takes a hit but males still want to mate.