Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsBlind mole-rats are loaded with anticancer genes
Genes of the long-lived blind mole-rat help explain how the animal evades cancer and why it lost vision.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryBacteria take plants to biofuel in one step
Engineered bacterium singlehandedly dismantles tough switchgrass molecules, making sugars that it ferments to make ethanol.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
AnimalsBeware the pregnant scorpion
Female striped bark scorpions are pregnant most of the time. That makes them fat, slow and really mean.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesIrish potato famine microbe traced to Mexico
The pathogen that triggered the Irish potato famine in the 1840s originated in central Mexico, not the Andes, as some studies had suggested.
-
 Oceans
OceansDusk heralds a feeding frenzy in the waters off Oahu
Even dolphins benefit when layers of organisms in the water column overlap for a short period.
-

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain’s support cells play role in hunger
Once considered just helpers for neurons, astrocytes sense the hormone leptin and can change mice’s appetites.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow a genetic quirk makes hair naturally blond
Natural blonds don’t need hair dye. They have a variation on a genetic enhancer that dampens pigment production in their hair follicles, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPets’ rights explored in ‘Citizen Canine’
Science journalist David Grimm describes pet's progression towards full citizenship.
-
-
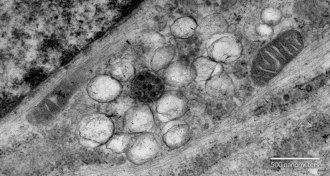 Life
LifeDrug candidate takes new aim at MERS
An experimental drug that shuts down construction of virus-making factories could become a new weapon against MERS.
By Meghan Rosen -
