Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHundreds of snake species get a new origin story
Elapoid snakes, including cobras, mambas and sea snakes, may have evolved in Asia, not Africa as many researchers once thought.
By Jake Buehler -
 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Then I Am Myself the World’ ponders what it means to be conscious
Neuroscientist Christof Koch’s new book discusses how information integration in the brain leads to consciousness and whether AI will ever be self-aware.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy a small seabird dares to fly toward cyclones
Tracking data show that Desertas petrels often veer toward cyclones and follow in their wake, perhaps to catch prey drawn to the surface.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPheromone fingers may help poison frogs mate
Specialized glands in the fingertips of some males may produce seductive chemical signals.
By Jake Buehler -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s blood tests are getting better, but still have a ways to go
Blood biomarker tests could help doctors know if a person's cognitive symptoms are due to Alzheimer's or something else.
-
 Animals
AnimalsStatic electricity may help butterflies and moths gather pollen on the fly
Electrostatically charged lepidopterans could draw pollen out of flowers without touching the blooms, computer simulations suggest.
By Anna Gibbs -
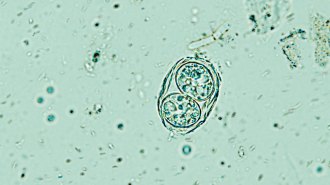 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGetting drugs into the brain is hard. Maybe a parasite can do the job
Researchers want to harness the parasite that causes toxoplasmosis to ferry drugs, but some question if the risks can be eliminated.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKomodo dragon teeth get their strength from an iron coat
Studying the reptile’s ironclad teeth in more detail could help solve a dinosaur dental mystery.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome melanoma cancer cells may punch their way through the body
A new study clarifies how melanoma cells use cell membrane protrusions called “blebs” to burrow through tissue.
By Claire Yuan -
 Oceans
OceansIn a seafloor surprise, metal-rich chunks may generate deep-sea oxygen
Instead of sinking from the surface, some deep-sea oxygen may be created by battery-like nodules that split water into hydrogen and oxygen.
By Sid Perkins -
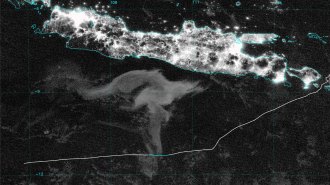 Oceans
OceansCan bioluminescent ‘milky seas’ be predicted?
For the first time, a scientist has used ocean and atmospheric data to find a milky sea, a huge expanse of luminous water, in past satellite images.
By Bas den Hond -
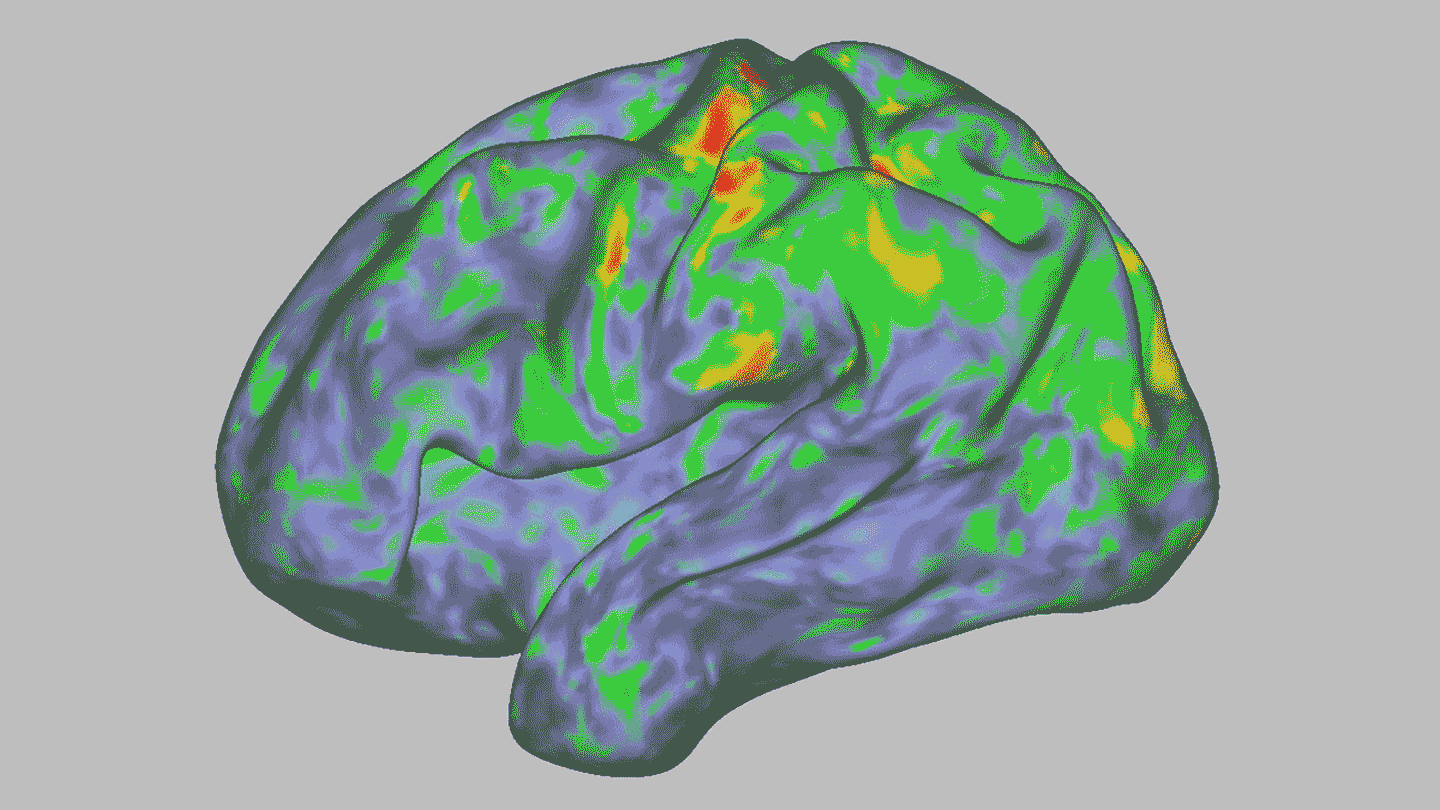 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePsilocybin temporarily dissolves brain networks
A high dose of the psychedelic drug briefly throws the brain off kilter. Other, longer-lasting changes could hint at psilocybin's therapeutic effects.