Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeBacteria’s tail spins make water droplets swirl
When bacteria band together, they can turn a fairly tame drop of water into a swirling vortex.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFish-eating spiders are the stuff of nightmares
Spiders that feast on fish can be found on every continent but Antarctica, a new review finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassenger pigeon population had booms and busts
DNA says the birds recovered from hard times — until people came along.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeAutoimmune diseases stopped in mice
Reprogramming immune cells may offer a way to treat autoimmune diseases without harming the body’s ability to fight infections.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSunbathing may boost endorphins in the body and brain
UV light makes mice churn out a molecule that is a cousin of morphine and heroin, a finding that may explain why some people seek out sunshine.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTriclosan may spoil wastewater treatment
Common antimicrobial could make microbes more drug resistant and less efficient at breaking down sewage sludge in municipal treatment plants.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple blood test detects heart transplant rejection
Heart transplant recipients whose bodies are starting to reject the new organ might carry genetic warning signs.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene variant tied to diabetes in Greenlanders
Greenlanders who carry two copies of a newly discovered gene variant have upwards of 10 times the chance of developing type 2 diabetes.
-
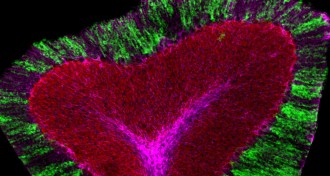 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStress hormone kicks brain cells into gear
Norepinephrine, a stress hormone, wakes up cells called astroglia, possibly shifting brain into vigilant state.
-
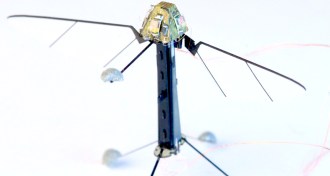 Tech
TechRobo-fly steadies flight with onboard sensor
Scaling a robot to the size of a fly and stabilizing its flight with onboard sensors offers clues to how live insects stay steady in mid-air.
-
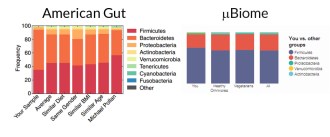 Life
LifeHere’s the poop on getting your gut microbiome analyzed
One Science News writer donated her used toilet paper for science and learned that microbiome research is as uncharted as the Wild West.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn emergencies, fire ants get lots of grips to form rafts
First look inside fire ant architecture shows how lots of leg grips assemble rafts, bridges and balls.
By Susan Milius