Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
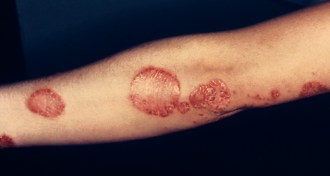
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Life
LifeGecko adhesion takes electric turn
Challenging a favored theory, measurements suggest that electrostatic interactions make gecko feet supersticky.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYet another reason to hate ticks
Ticks are tiny disease-carrying parasites that should also be classified as venomous animals, a new study argues.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDuck-billed dinosaurs roamed the Arctic in herds
Young and old duck-billed dinosaurs lived together in herds in the Arctic, tracks preserved in Alaska indicate.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal largest airborne bird
Despite its massive size, an extinct bird may have been an efficient glider.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMicroplastics lodge in crab gills and guts
Crabs can absorb microplastic particles through their gills and by eating polluted mussels.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsIf you really hate a species, try eating it
Dining on invasive fish such as snakehead and lionfish can reduce their numbers, but we can’t entirely eat our way out this problem.
-
 Climate
ClimateMeat-eaters’ greenhouse gas emissions are twice as high as vegans’
Meat-eaters dietary GHG emissions are twice as high as those of vegans, a study finds.
-
 Animals
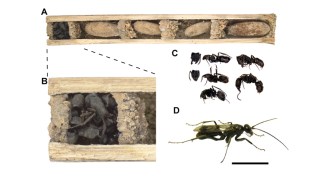
AnimalsDead-ant wall protects young spider wasps
Bone-house wasps probably use a barrier of deceased insects to guard against predators.
-
 Neuroscience
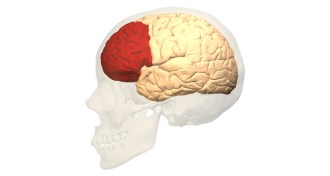
NeuroscienceMRI scans reveal how the brain tells the body to pee
Scientists see heightened brain activity in men right before they urinate.
-
 Life
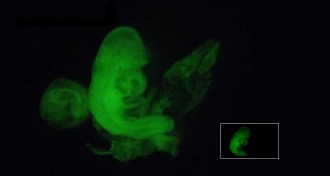
LifeDramatic retraction adds to questions about stem cell research
Researchers who reported an easy method for making stem cells admit mistakes mar their work, and have retracted their papers from Nature.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMantis shrimp tune their eyes with sunscreen
Blocking some rays in just the right way creates six ways of actually seeing ultraviolet light.